The Arrhythmogenic Calmodulin Mutation D129G Dysregulates Cell Growth, Calmodulin-dependent Kinase II Activity, and Cardiac Function in Zebrafish
- PMID: 27815504
- PMCID: PMC5207174
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.758680
The Arrhythmogenic Calmodulin Mutation D129G Dysregulates Cell Growth, Calmodulin-dependent Kinase II Activity, and Cardiac Function in Zebrafish
Abstract
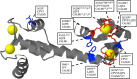
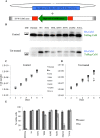
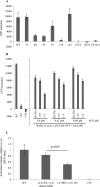
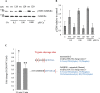
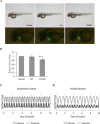
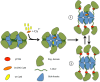
Calmodulin (CaM) is a Ca2+ binding protein modulating multiple targets, several of which are associated with cardiac pathophysiology. Recently, CaM mutations were linked to heart arrhythmia. CaM is crucial for cell growth and viability, yet the effect of the arrhythmogenic CaM mutations on cell viability, as well as heart rhythm, remains unknown, and only a few targets with relevance for heart physiology have been analyzed for their response to mutant CaM. We show that the arrhythmia-associated CaM mutants support growth and viability of DT40 cells in the absence of WT CaM except for the long QT syndrome mutant CaM D129G. Of the six CaM mutants tested (N53I, F89L, D95V, N97S, D129G, and F141L), three showed a decreased activation of Ca2+/CaM-dependent kinase II, most prominently the D129G CaM mutation, which was incapable of stimulating Thr286 autophosphorylation. Furthermore, the CaM D129G mutation led to bradycardia in zebrafish and an arrhythmic phenotype in a subset of the analyzed zebrafish.
Keywords: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII); DT40; calcium; calmodulin (CaM); catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT); cell signaling; heart failure.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Berchtold M. W., Brinkmeier H., and Müntener M. (2000) Calcium ion in skeletal muscle: its crucial role for muscle function, plasticity, and disease. Physiol. Rev. 80, 1215–1265 - PubMed
-
- Berchtold M. W., and Villalobo A. (2014) The many faces of calmodulin in cell proliferation, programmed cell death, autophagy, and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1843, 398–435 - PubMed
-
- Berchtold M. W., Egli R., Rhyner J. A., Hameister H., and Strehler E. E. (1993) Localization of the human bona fide calmodulin genes CALM1, CALM2, and CALM3 to chromosomes 14q24-q31, 2p21.1-p21.3, and 19q13.2-q13.3. Genomics 16, 461–465 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

