Body Region Involvement and Quality of Life in Psoriasis: Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial of Adalimumab
- PMID: 27815915
- PMCID: PMC5110581
- DOI: 10.1007/s40257-016-0229-x
Body Region Involvement and Quality of Life in Psoriasis: Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial of Adalimumab
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis severity and treatment responsiveness vary by body region, which differentially impacts quality of life (QoL).
Objective: The objective of the study was to examine adalimumab efficacy by body region and regional response and QoL relationship.
Methods: Patients (n = 1212) with moderate-to-severe psoriasis were randomized 2:1 to 80 mg at week 0, followed by adalimumab 40 mg or placebo every other week for 16 weeks in the double-blind REVEAL study. Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) responses and Dermatology Life Quality Index outcomes were analyzed.
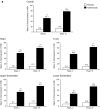
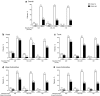
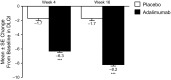
Results: Week 16 regional mean PASI improvements were significantly greater with adalimumab (83.1 ± 1.57, 81.3 ± 1.58, 75.7 ± 1.34, and 73.9 ± 1.26% in the trunk, head, upper extremities, and lower extremities, respectively; all p < 0.001 vs. placebo). Likewise, percentages of patients with regional PASI ≥75/≥90/100% reduction from baseline were significantly higher with adalimumab (all p < 0.001); adalimumab responses were greater for the trunk (77.9/65.0/59.1%) and head (74.6/66.1/62.8%; all p ≤ 0.0001 vs. lower) than upper (67.7/45.1/39.6%; p = 0.4, p = 0.04, p = 0.0005, respectively, vs. lower) and lower extremities (65.7/40.0/31.3%). Adalimumab significantly improved Dermatology Life Quality Index scores vs. placebo (8.2- vs 1.7-point decrease from baseline; p < 0.001).
Limitations: The study was a post hoc analysis.
Conclusions: Adalimumab treatment resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in disease severity and QoL. QoL improvements were associated with PASI responses in all body regions.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT00237887.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical StandardsFundingAbbVie Inc. funded the study (NCT00237887), contributed to its design, and was involved in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data, and in the writing, review, and approval of the publication.Conflict of interestApril W. Armstrong serves as an investigator and/or consultant for AbbVie Inc., Amgen, Janssen, Merck, Lilly, Celgene, Novartis, Pfizer, and Modernizing Medicine. Delfina Guadalupe Villanueva Quintero has served as a consultant and speaker for UCB Pharma, Leo Pharma, Pfizer, and AbbVie Inc. Cristina M. Echeverría has served as a consultant and speaker for AbbVie Inc. and UCB Pharma. Yihua Gu, Mahinda Karunaratne, and Ofelia Reyes Servín are employees of AbbVie Inc. and may own AbbVie Inc. stock and/or stock options.Ethics approval and consent to participateThis is a post hoc analysis of a previously published study (Menter et al. Adalimumab therapy for moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a randomized, controlled phase III trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:106-115). The original study was conducted in accordance with the protocol, International Conference on Harmonisation guidelines, applicable regulations and guidelines governing clinical study conduct, and the ethical principles that have their origin in the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.Written informed consent for the original study was obtained from all individual participants.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

