Differential Effects of Environmental and Genetic Factors on T and B Cell Immune Traits
- PMID: 27818087
- PMCID: PMC5130901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.053
Differential Effects of Environmental and Genetic Factors on T and B Cell Immune Traits
Abstract
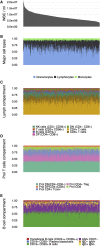
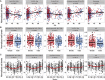
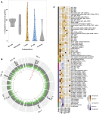
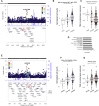
Effective immunity requires a complex network of cellular and humoral components that interact with each other and are influenced by different environmental and host factors. We used a systems biology approach to comprehensively assess the impact of environmental and genetic factors on immune cell populations in peripheral blood, including associations with immunoglobulin concentrations, from ∼500 healthy volunteers from the Human Functional Genomics Project. Genetic heritability estimation showed that variations in T cell numbers are more strongly driven by genetic factors, while B cell counts are more environmentally influenced. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping identified eight independent genomic loci associated with leukocyte count variation, including four associations with T and B cell subtypes. The QTLs identified were enriched among genome-wide association study (GWAS) SNPs reported to increase susceptibility to immune-mediated diseases. Our systems approach provides insights into cellular and humoral immune trait variability in humans.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Akiyama M., Suzuki K., Yamaoka K., Yasuoka H., Takeshita M., Kaneko Y., Kondo H., Kassai Y., Miyazaki T., Morita R. Number of Circulating Follicular Helper 2 T Cells Correlates With IgG4 and Interleukin-4 Levels and Plasmablast Numbers in IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2476–2481. - PubMed
-
- Amadori A., Zamarchi R., De Silvestro G., Forza G., Cavatton G., Danieli G.A., Clementi M., Chieco-Bianchi L. Genetic control of the CD4/CD8 T-cell ratio in humans. Nat. Med. 1995;1:1279–1283. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J.R. Stat. Soc. 1995;57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

