Resisting Resistance: Targeted Therapies in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 27819059
- PMCID: PMC5091655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.05.010
Resisting Resistance: Targeted Therapies in Lung Cancer
Abstract
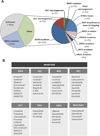
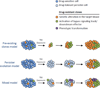
Drug resistance inevitably limits the efficacy of all targeted therapies including tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Understanding the biological underpinnings of TKI resistance is key to the successful development of future therapeutic strategies. Traditionally, mechanisms of TKI resistance have been viewed under a dichotomous lens. Tumor cells are TKI-sensitive or TKI-refractory, exhibit intrinsic or acquired resistance, and accumulate alterations within or outside the target to promote their survival. Such classifications facilitate our comprehension of an otherwise complex biology, but are likely an oversimplification. Recent studies underscore the multifaceted, genetically heterogeneous nature of TKI resistance, which evolves dynamically with changes in therapy. In this Review, we provide a broad framework for understanding the diverse mechanisms of resistance at play in oncogene-driven lung cancers.
Keywords: NSCLC; Resistance; tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI).
Figures
References
-
- Weinstein IB. Addiction to oncogenes –the Achilles heal of cancer. Science. 2002;297:63–64. - PubMed
-
- Camidge DR, et al. Acquired resistance to TKIs in solid tumours: learning from lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014;11:473–481. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;362:2380–2388. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
