Piphillin: Improved Prediction of Metagenomic Content by Direct Inference from Human Microbiomes
- PMID: 27820856
- PMCID: PMC5098786
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166104
Piphillin: Improved Prediction of Metagenomic Content by Direct Inference from Human Microbiomes
Abstract
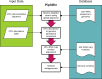
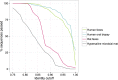
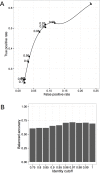
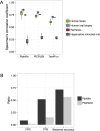
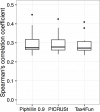
Functional analysis of a clinical microbiome facilitates the elucidation of mechanisms by which microbiome perturbation can cause a phenotypic change in the patient. The direct approach for the analysis of the functional capacity of the microbiome is via shotgun metagenomics. An inexpensive method to estimate the functional capacity of a microbial community is through collecting 16S rRNA gene profiles then indirectly inferring the abundance of functional genes. This inference approach has been implemented in the PICRUSt and Tax4Fun software tools. However, those tools have important limitations since they rely on outdated functional databases and uncertain phylogenetic trees and require very specific data pre-processing protocols. Here we introduce Piphillin, a straightforward algorithm independent of any proposed phylogenetic tree, leveraging contemporary functional databases and not obliged to any singular data pre-processing protocol. When all three inference tools were evaluated against actual shotgun metagenomics, Piphillin was superior in predicting gene composition in human clinical samples compared to both PICRUSt and Tax4Fun (p<0.01 and p<0.001, respectively) and Piphillin's ability to predict disease associations with specific gene orthologs exhibited a 15% increase in balanced accuracy compared to PICRUSt. From laboratory animal samples, no performance advantage was observed for any one of the tools over the others and for environmental samples all produced unsatisfactory predictions. Our results demonstrate that functional inference using the direct method implemented in Piphillin is preferable for clinical biospecimens. Piphillin is publicly available for academic use at http://secondgenome.com/Piphillin.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported in part by Second Genome Inc and Allergan PLC. Neil Poloso is employed by Allergen PLC and holds stock options. Shoko Iwai, Thomas Weinmaier, Karim Dabbagh, and Todd DeSantis are employed by Second Genome Inc. and hold stock options. Both Allergan PLC and Second Genome Inc. are independent therapeutics companies with products in development to treat gastrointestinal disorders and other human diseases. A publication announcing the availability of PiPhillin analysis for academic use will not affect the value of our therapeutic products. There are no PiPhillin patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. Second Genome, Inc. provides a commercial microbiome profiling service using software with demonstrable accuracy such as PiPhillin. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the guide for authors.
Figures

References
-
- Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, Lakhdari O, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Gratadoux J-J, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105: 16731–6. 10.1073/pnas.0804812105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

