Suppression of Type I IFN Signaling in Tumors Mediates Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Treatment That Can Be Overcome by Radiotherapy
- PMID: 27821490
- PMCID: PMC5875182
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3142
Suppression of Type I IFN Signaling in Tumors Mediates Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Treatment That Can Be Overcome by Radiotherapy
Abstract
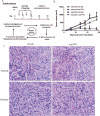
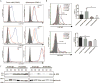
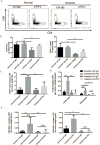
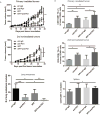
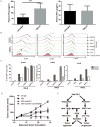
Immune checkpoint therapies exhibit impressive efficacy in some patients with melanoma or lung cancer, but the lack of response in most cases presses the question of how general efficacy can be improved. In addressing this question, we generated a preclinical tumor model to study anti-PD-1 resistance by in vivo passaging of Kras-mutated, p53-deficient murine lung cancer cells (p53R172HΔg/+K-rasLA1/+ ) in a syngeneic host exposed to repetitive dosing with anti-mouse PD-1 antibodies. PD-L1 (CD274) expression did not differ between the resistant and parental tumor cells. However, the expression of important molecules in the antigen presentation pathway, including MHC class I and II, as well as β2-microglobulin, were significantly downregulated in the anti-PD-1-resistant tumors compared with parental tumors. Resistant tumors also contained fewer CD8+ (CD8α) and CD4+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and reduced production of IFNγ. Localized radiotherapy induced IFNβ production, thereby elevating MHC class I expression on both parental and resistant tumor cells and restoring the responsiveness of resistant tumors to anti-PD-1 therapy. Conversely, blockade of type I IFN signaling abolished the effect of radiosensitization in this setting. Collectively, these results identify a mechanism of PD-1 resistance and demonstrate that adjuvant radiotherapy can overcome resistance. These findings have immediate clinical implications for extending the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint therapy in patients. Cancer Res; 77(4); 839-50. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
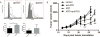
Similar articles
-
A Combined PD-1/C5a Blockade Synergistically Protects against Lung Cancer Growth and Metastasis.Cancer Discov. 2017 Jul;7(7):694-703. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1184. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Cancer Discov. 2017. PMID: 28288993
-
Combined Radiotherapy and Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Synergistically Enhances Antitumor Effect in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Jul;12(7):1085-1097. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.04.014. Epub 2017 May 3. J Thorac Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28478231
-
Response to Programmed Cell Death-1 Blockade in a Murine Melanoma Syngeneic Model Requires Costimulation, CD4, and CD8 T Cells.Cancer Immunol Res. 2016 Oct;4(10):845-857. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0060. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27589875 Free PMC article.
-
Novel strategies for inhibiting PD-1 pathway-mediated immune suppression while simultaneously delivering activating signals to tumor-reactive T cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015 Oct;64(10):1287-93. doi: 10.1007/s00262-015-1677-5. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25792524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy for Tumors with Downregulated MHC Class I Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 21;18(6):1331. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061331. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28635644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting MHC-I molecules for cancer: function, mechanism, and therapeutic prospects.Mol Cancer. 2023 Dec 2;22(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01899-4. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38041084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mode-of-Action of Targeted Alpha Therapy Radium-223 as an Enabler for Novel Combinations to Treat Patients with Bone Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 10;20(16):3899. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163899. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31405099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined radiotherapy with nivolumab for extracranial metastatic malignant melanoma.Jpn J Radiol. 2018 Dec;36(12):712-718. doi: 10.1007/s11604-018-0774-8. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Jpn J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30206802
-
Immune checkpoint modulators in cancer immunotherapy: recent advances and emerging concepts.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Aug 17;15(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01325-0. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35978433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance mechanisms in melanoma to immuneoncologic therapy with checkpoint inhibitors.Cancer Drug Resist. 2019 Sep 19;2(3):744-761. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.28. eCollection 2019. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 35582566 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

