Classification systems for chronic graft-versus-host disease
- PMID: 27821503
- PMCID: PMC5216262
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-07-686642
Classification systems for chronic graft-versus-host disease
Abstract
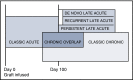
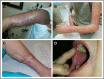
Chronic graft versus host disease (GVHD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clinically, chronic GVHD is a pleiotropic, multiorgan syndrome involving tissue inflammation and fibrosis that often results in permanent organ dysfunction. Chronic GVHD is fundamentally caused by replacement of the host's immune system with donor cells, although the heterogeneity of clinical manifestations suggests that patient, donor, and transplant factors modulate the phenotype. The diagnosis of chronic GVHD and determination of treatment response largely rely on clinical examination and patient interview. The 2005 and 2014 National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Projects on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic GVHD standardized the terminology around chronic GVHD classification systems to ensure that a common language and procedures are being used in clinical research. This review provides a summary of these recommendations and illustrates how they are being used in clinical research and the potential for their use in clinical care.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


References
-
- Lee SJ, Flowers ME. Recognizing and managing chronic graft-versus-host disease. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2008;2008:134-141. - PubMed
-
- Socié G, Stone JV, Wingard JR, et al. ; Late Effects Working Committee of the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry. Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(1):14-21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

