Promotion of the transdermal delivery of protein drugs by N-trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles combined with polypropylene electret
- PMID: 27822034
- PMCID: PMC5087780
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S109552
Promotion of the transdermal delivery of protein drugs by N-trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles combined with polypropylene electret
Abstract
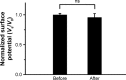
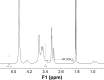
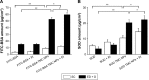
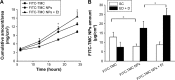
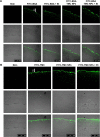
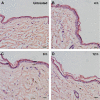
We recently reported that electret, which was prepared by a corona charging system with polypropylene film, could enhance the transdermal delivery of several drugs of low molecular weight. The aim of this study was to investigate whether electret could enhance the transdermal delivery of protein drugs by N-trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles (TMC NPs) prepared by an ionic gelation method. A series of experiments were performed, including in vitro skin permeation assays and anti-inflammatory effects, to evaluate the transdermal delivery of protein drugs by TMC NPs in the presence of electret. The results showed that in the presence of electret, the transdermal delivery of protein drugs in TMC NPs was significantly enhanced, as demonstrated by in vitro permeation studies and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Notably, superoxide dismutase-loaded TMC NPs combined with electret exhibited the best inhibitory effect on the edema of the mouse ear. TMC NPs combined with electret represent a novel platform for the transdermal delivery of protein drugs.
Keywords: N-trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles; electret; protein drugs; transdermal delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


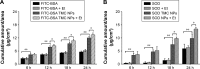


Similar articles
-
Colonic targeting insulin-loaded trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles coated pectin for oral delivery: In vitro and In vivo studies.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;281(Pt 4):136549. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136549. Epub 2024 Oct 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39401622
-
Chitosan nanoconstructs for improved oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin: In vitro and in vivo evaluation.Int J Pharm. 2012 Jan 17;422(1-2):179-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.10.048. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Int J Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22079712
-
Efficient mucus permeation and tight junction opening by dissociable "mucus-inert" agent coated trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery.J Control Release. 2016 Jan 28;222:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.008. Epub 2015 Dec 11. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26686663
-
N,N,N-Trimethyl chitosan: An advanced polymer with myriad of opportunities in nanomedicine.Carbohydr Polym. 2017 Feb 10;157:875-902. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.041. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Carbohydr Polym. 2017. PMID: 27988003 Review.
-
Delving Deeper into Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery: Factors and Mechanisms Associated with Nanocarrier-mediated Strategies.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(27):3210-3222. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180924122640. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30246632 Review.
Cited by
-
Chitosan Nanocarrier Entrapping Hydrophilic Drugs as Advanced Polymeric System for Dual Pharmaceutical and Cosmeceutical Application: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Box-Behnken Design.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;13(5):677. doi: 10.3390/polym13050677. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668161 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic/electrical dual stimulation response nanocomposite bioelectret for controlled precision drug release.Mater Today Bio. 2023 May 13;20:100665. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100665. eCollection 2023 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 37229214 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-Based Multifunctional Platforms for Local Delivery of Therapeutics.Mar Drugs. 2017 Mar 1;15(3):60. doi: 10.3390/md15030060. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28257059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomedical Applications of Electrets: Recent Advance and Future Perspectives.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jun 12;14(6):320. doi: 10.3390/jfb14060320. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37367284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancements in Non-Invasive Formulations for Protein Drug Delivery.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Sep 11;17:1290-1308. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.09.004. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31921395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi WI, Lee JH, Kim JY, Kim JC, Kim YH, Tae G. Efficient skin permeation of soluble proteins via flexible and functional nano-carrier. J Contr Rel. 2012;157(2):272–278. - PubMed
-
- Karande P, Jain A, Mitragotri S. Discovery of transdermal penetration enhancers by high-throughput screening. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22(2):192–197. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Hao TN, Ding PT, et al. Effect of pH, vehicles and chemical enhancers on the skin permeation of loratadine. Lat Am J Pharm. 2011;30(3):534–539.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

