The Danish Hysterectomy and Hysteroscopy Database
- PMID: 27822093
- PMCID: PMC5094637
- DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S99465
The Danish Hysterectomy and Hysteroscopy Database
Abstract
Aim of the database: The steering committee of the Danish Hysterectomy and Hysteroscopy Database (DHHD) has defined the objective of the database: the aim is firstly to reduce complications, readmissions, reoperations; secondly to specify the need for hospitalization after hysterectomy; thirdly to secure quality assessment of hysterectomy and hysteroscopy by setting standards and national guidelines; and finally to intensify the monitoring of laparoscopic surgery and explore long-term side effects after hysterectomy.
Study population: We include all women in Denmark who have had elective benign uterine surgery since 2003. The surgery includes hysterectomy and operative hysteroscopy. In the latter, we include resection of the endometrium and submucosal leiomyomas and ablations of the endometrium.
Main variables: Detailed information about the hysterectomy and hysteroscopy operation techniques, cooperations, and indications is registered directly in the National Patient Register (NPR), as well as relevant lifestyle factors and confounders. It is mandatory to register information about complications and readmissions in the NPR. Data included in DHHD are directly extracted from the NPR.
Descriptive data: Annually approximately 4,300 hysterectomies and 3,200 operative hysteroscopies are performed in Denmark. Since the establishment of the database in 2003, 50,000 hysterectomies have been registered. DHHD's nationwide cooperation and research have led to national guidelines and regimes. Annual national meetings and nationwide workshops have been organized.
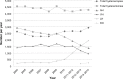
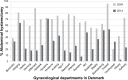
Conclusion: The use of vaginal and laparoscopic hysterectomy methods has increased during the past decade and the overall complication rate and hospital stay have declined. The regional variation in operation methods has also decreased.
Keywords: clinical quality register; complication; epidemiology; gynecology; laparoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Nielsen SL, Daugbjerg SB, Gimbel H, Settnes A. Use of vaginal hysterectomy in Denmark: rates, indications and patient characteristics. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011;90(9):978–984. - PubMed
-
- Moller C, Kehlet H, Utzon J, Ottesen B. Hysterectomy in Denmark. An analysis of postoperative hospitalisation, morbidity and readmission. Dan Med Bull. 2002;49(4):353–357. - PubMed
-
- Hansen CT, Moller C, Daugbjerg S, Utzon J, Kehlet H, Ottesen B. Establishment of a national Danish hysterectomy database: preliminary report on the first 13,425 hysterectomies. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008;87(5):546–557. - PubMed
-
- Dansk Hysterektomi og Hysteroskopi Databases, Hyskorapport 2004–2006 [The Danish Hysterectomy and Hysteroscopy Database: Report of Hysteroscopy in Denmark 2004–2006] [Accessed November, 2013]. Available from: http://gynobsguideline.dk/files/HyskobaseAarsrapport%202004%20-%202006.pdf.
-
- Utzon J, Hansen CC, Andreasen J, Ottesen BS. Dansk Hysterektomi Database set i et sundhedsøkonomisk perspektiv [The Danish Hysterectomy Database seen from a public health-economic perspective] Ugeskr Laeger. 2005;167(34):3170–3174. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

