The Danish Neuro-Oncology Registry
- PMID: 27822109
- PMCID: PMC5094636
- DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S99459
The Danish Neuro-Oncology Registry
Abstract
Aim of database: The Danish Neuro-Oncology Registry (DNOR) was established by the Danish Neuro-Oncology Group as a national clinical database. It was established for the purpose of supporting research and development in adult patients with primary brain tumors in Denmark.
Study population: DNOR has registered clinical data on diagnostics and treatment of all adult patients diagnosed with glioma since January 1, 2009, which numbers approximately 400 patients each year.
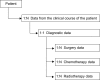
Main variables: The database contains information about symptoms, presurgical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) characteristics, performance status, surgical procedures, residual tumor on postsurgical MRI, postsurgical complications, diagnostic and histology codes, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy.
Descriptive data: DNOR publishes annual reports on descriptive data. During the period of registration, postoperative MRI is performed in a higher proportion of the patients (Indicator II), and a higher proportion of patients have no residual tumor after surgical resection of the primary tumor (Indicator IV). Further data are available in the annual reports. The indicators reflect only minor elements of handling brain tumor patients. Another advantage of reporting indicators is the related multidisciplinary discussions giving a better understanding of what actually is going on, thereby facilitating the work on adjusting the national guidelines in the Danish Neuro-Oncology Group.
Conclusion: The establishment of DNOR has optimized the quality in handling primary brain tumor patients in Denmark by reporting indicators and facilitating a better multidisciplinary collaboration at a national level. DNOR provides a valuable resource for research.
Keywords: brain cancer; brain neoplasms; clinical quality indicators; glioma.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- DNOG.dk [homepage on the Internet] The Danish Neuro-Oncology Registry. [Accessed November 19, 2015]. Available from: http://www.dnog.dk/database.
-
- DNOG.dk [homepage on the Internet] The Danish Neuro-Oncology Registry. [Accessed November 19, 2015]. Available from: http://www.dnog.dk/assets/files/Retningslinier%20PDF/DNOG-2014-Gliom-Ret....
-
- WHO.int [homepage on the Internet] World Health Organization. [Accessed November 19, 2015]. Available from: http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/
-
- Patobank.dk [homepage on the Internet] The Danish Pathology Register. [Accessed November 19, 2015]. Available from: http://www.patobank.dk/index.php?ID=18&lang=da.
-
- Pedersen CB. The Danish Civil Registration System. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39(7 Suppl):22–25. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials