Hemorheological Alteration in Patients Clinically Diagnosed with Chronic Liver Diseases
- PMID: 27822933
- PMCID: PMC5102858
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.12.1943
Hemorheological Alteration in Patients Clinically Diagnosed with Chronic Liver Diseases
Abstract
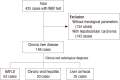
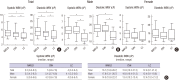
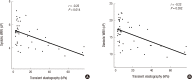
Since liver function is changed by chronic liver diseases, chronic liver disease can lead to different hemorheological alterations during the course of the progression. This study aims to compare alterations in whole blood viscosity in patients with chronic liver disease, focusing on the gender effect. Chronic liver diseases were classified into three categories by patient's history, serologic markers, and radiologic findings: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (n = 63), chronic viral hepatitis B and C (n = 50), and liver cirrhosis (LC) (n = 35). Whole blood viscosity was measured by automated scanning capillary tube viscometer, while liver stiffness was measured by transient elastography using FibroScan®. Both systolic and diastolic whole blood viscosities were significantly lower in patients with LC than NAFLD and chronic viral hepatitis (P < 0.001) in male patients, but not in female patients. In correlation analysis, there were inverse relationships between both systolic and diastolic whole blood viscosity and liver stiffness (systolic: r = -0.25, diastolic: r = -0.22). Whole blood viscosity was significantly lower in male patients with LC than NAFLD or chronic viral hepatitis. Our data suggest that whole blood viscosity test can become a useful tool for classifying chronic liver disease and determining the prognosis for different types of chronic liver diseases.
Keywords: Chronic Liver Disease; Hemorheology; Whole Blood Viscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Omoti CE, Omuemu CE, Olu-Eddo AN. The rheological profile of chronic liver disease patients in Nigeria. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2009;42:279–284. - PubMed
-
- Tamer S, Cefle K, Gokkusu C, Ademoglu E, Ozturk S, Vatansever S, Palanduz S, Guler K. Comparison of rheological parameters in patients with post hepatitic and alcoholic cirrhosis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2007;36:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Anwar MA, Rampling MW. Abnormal hemorheological properties in patients with compensated and decompensated hepatic cirrhosis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2003;29:95–101. - PubMed
-
- Tripodi A, Mannucci PM. The coagulopathy of chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Baskurt OK, Meiselman HJ. Blood rheology and hemodynamics. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2003;29:435–450. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

