Length-free near infrared measurement of newborn malnutrition
- PMID: 27824061
- PMCID: PMC5099907
- DOI: 10.1038/srep36052
Length-free near infrared measurement of newborn malnutrition
Abstract
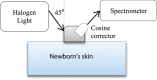
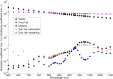
Under-nutrition in neonates can cause immediate mortality, impaired cognitive development and early onset adult disease. Body fat percentage measured using air-displacement-plethysmography has been found to better indicate under-nutrition than conventional birth weight percentiles. However, air-displacement-plethysmography equipment is expensive and non-portable, so is not suited for use in developing communities where the burden is often the greatest. We proposed a new body fat measurement technique using a length-free model with near-infrared spectroscopy measurements on a single site of the body - the thigh. To remove the need for length measurement, we developed a model with five discrete wavelengths and a sex parameter. The model was developed using air-displacement-plethysmography measurements in 52 neonates within 48 hours of birth. We identified instrumentation required in a low-cost LED-based screening device and incorporated a receptor device that can increase the amount of light collected. This near-infrared method may be suitable as a low cost screening tool for detecting body fat levels and monitoring nutritional interventions for malnutrition in neonates and young children in resource-constrained communities.
Conflict of interest statement
This project was funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation Grand Challenges Scheme OPP1111820. All authors received a salary or scholarship funding from The University of Sydney who have filed a provisional patent. The authors declare that they are bound by confidentiality agreements that prevent them from disclosing their financial interests in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Levitsky D. A. & Strupp B. J. Malnutrition and the brain: changing concepts, changing concerns. The Journal of nutrition 125, 2212S–2220S (1995). - PubMed
-
- Organization W. H. World health statistics 2010. (World Health Organization, 2010).
-
- Carberry A. E., Raynes-Greenow C. H., Turner R. M., Askie L. M. & Jeffery H. E. Is body fat percentage a better measure of undernutrition in newborns than birth weight percentiles? Pediatric research 74, 730–736 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Christensen K. & Kushner R. Measuring body fat in the clinical setting. Obesity Management 3, 93–95 (2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

