Demethylation of MicroRNA-124a Genes Attenuated Proliferation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Derived Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and Synthesis of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
- PMID: 27824863
- PMCID: PMC5100945
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164207
Demethylation of MicroRNA-124a Genes Attenuated Proliferation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Derived Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and Synthesis of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
Abstract
Objective: To examine the impact of 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-AzadC) on methylation status of miR-124a genes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) associated fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and its effect on RA-FLS proliferation and TNF-α expression.
Materials and methods: FLS were isolated from seven RA-derived synovial tissues and cultured in vitro. The expression of miR-124a was measured by real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in FLS with or without 5-AzadC treatment. MiR-124a gene methylation was detected by methylation-specific PCR. FLS were divided into three groups as control, IL-1β and IL-1β/5-AzadC, respectively. The cells in the IL-1β group were treated with 5 μg/L of IL-1β for 24 hours, whereas the cells in the IL-1β/5-AzadC group were first treated with IL-1β exactly as those in the IL-1β group for 24 h but further treated with 1μM 5-AzadC for additional 3 days. The cell growth was estimated based on absorbance at UV450nm. Secreted TNF-α from the cells was evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. After that, RA-FLS treated with IL-1β plus 5-AzadC were further transfected with miR-124a inhibitor or scrambled control. After culturing for 3 days, cell growth and TNF-α concentrations were measured.
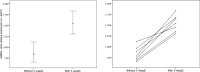
Results: After 5-AzadC treatment, the expression of miR-124a was significantly increased compared with the control group (1.545 ± 0.189 vs 0.836 ± 0.166, p = 0.001). On the other hand, 5-AzadC significantly reduced IL-1β-mediated cell proliferation by nearly 2.5 fold (p = 0.006). Also, the level of TNF-α secreted from the cells treated with IL-1β plus 5-AzadC was considerably less than that from the cells treated with IL-1β alone (324.99 ± 22.73 ng/L vs 387.91 ± 58.51 ng/L, p = 0.022). After transfection with miR-124a inhibitor in RA-FLS treated with IL-1β plus 5-AzadC, the cell proliferation was increased by 18.2% and the TNF-α expression was increased by 19.0% (p = 0.001 and 0.011, respectively).
Conclusion: Methylation of miR-124a genes contributed to IL-1β-mediated RA-FLS proliferation and TNF-α expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Paeonol protects against TNF-α-induced proliferation and cytokine release of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by upregulating FOXO3 through inhibition of miR-155 expression.Inflamm Res. 2017 Jul;66(7):603-610. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1041-7. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Inflamm Res. 2017. PMID: 28401267
-
miR-124a inhibits the proliferation and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via targeting PIK3/NF-κB pathway.Cell Biochem Funct. 2019 Jun;37(4):208-215. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3386. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Cell Biochem Funct. 2019. PMID: 30941802
-
Genistein inhibit cytokines or growth factor-induced proliferation and transformation phenotype in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis.Inflammation. 2012 Feb;35(1):377-87. doi: 10.1007/s10753-011-9365-x. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 21792602
-
miR-124a as a key regulator of proliferation and MCP-1 secretion in synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Mar;70 Suppl 1:i88-91. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.138669. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21339227 Review.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase gene BIRC3 modulates TNF-induced cell death pathways and promotes aberrant proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1433898. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433898. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring regulatory mechanisms on miRNAs and their implications in inflammation-related diseases.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jul 3;24(1):142. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01334-y. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38958690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA Expression Profiles in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Emerging Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 23;12:792884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.792884. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Changes in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 14;10:570. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00570. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31258550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Treatment with the Hypomethylating Agent 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine in Murine Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Nov 27;12(4):174. doi: 10.3390/ph12040174. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31783688 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miR‑124a as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in non‑small cell lung cancer for chemotherapy.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jul;16(1):238-246. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6595. Epub 2017 May 17. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28534972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamachi Y, Kawano S, Takenokuchi M, Nishimura K, Sakai Y, Chin T, et al. MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:1294–304 10.1002/art.24475 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

