Inhibiting the proton pump: mechanisms, benefits, harms, and questions
- PMID: 27825384
- PMCID: PMC5101661
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-016-0724-1
Inhibiting the proton pump: mechanisms, benefits, harms, and questions
Abstract
Inhibition of the H+/K+-adenosine triphosphatase (the proton pump) is the final common mechanistic pathway in reducing gastric acid secretion pharmacologically. Proton pump inhibitors are widely used in upper gastrointestinal diseases, including gastric and duodenal ulcers, eradication of Helicobacter pylori in combination with antibiotics, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced peptic ulceration. Reviewing their benefits and harms in BMC Medicine, Scarpignato et al. report effectiveness in these conditions, and harms that are generally mild and uncommon (1-3 %). Serious adverse reactions, such as tubulointerstitial nephritis, are rare. However, the risks of gastric and pancreatic cancer are unclear. Drug-drug interactions can occur through effects on P glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes. Several questions remain. Do all proton pump inhibitors carry the same risks of serious adverse reactions? Which individuals are most susceptible? What are the time courses of individual reactions? What monitoring strategies are best? New drugs for the same indications continue to emerge, including potassium-competitive acid blockers, inhibitors of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation, serotonergic agents/prokinetics, mucosal protectants, histamine H3 receptor agonists, anti-gastrin agents, and esophageal pain modulators. Their benefit to harm balance remains to be discovered.Please see related article: https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-016-0718-z.
Keywords: Adverse drug reactions; Benefits; Drug–drug interactions; Harms; Proton pump inhibitors.
Figures
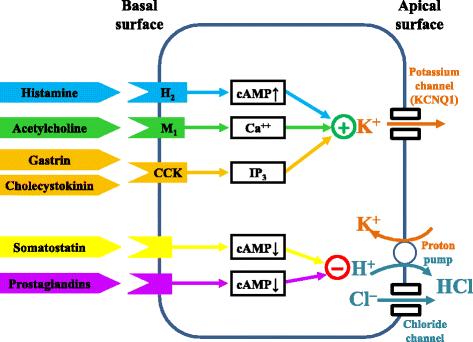
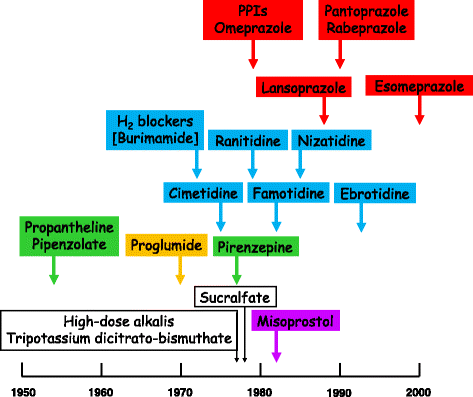
Comment on
-
Effective and safe proton pump inhibitor therapy in acid-related diseases - A position paper addressing benefits and potential harms of acid suppression.BMC Med. 2016 Nov 9;14(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12916-016-0718-z. BMC Med. 2016. PMID: 27825371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kumagai K, Hiki N, Nunobe S, Jiang X, Kubota T, Aikou S, Watanabe R, Tanimura S, Sano T, Kitagawa Y, Yamaguchi T. Different features of complications with Billroth-I and Roux-en-Y reconstruction after laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15(12):2145–2152. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1683-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

