Characterization of anti-MERS-CoV antibodies against various recombinant structural antigens of MERS-CoV in an imported case in China
- PMID: 27826140
- PMCID: PMC5148018
- DOI: 10.1038/emi.2016.114
Characterization of anti-MERS-CoV antibodies against various recombinant structural antigens of MERS-CoV in an imported case in China
Abstract
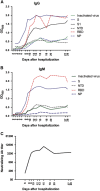
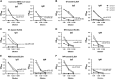
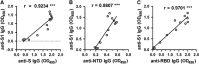
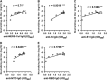
The first imported case of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) in China recently occurred, allowing for the characterization of antibody titers in a series of the patient's sera using the following methods based on recombinant viral structural antigens: inactivated MERS coronavirus (MERS-CoV) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), recombinant MERS-CoV spike (S, or fragments of S) ELISA, nucleoprotein (NP) ELISA and MERS S pseudovirus particle-based neutralization test (ppNT). A longitudinal profile of the infection showed that seroconversion detected by ELISAs based on the recombinant extracellular domain, S, S1 and receptor-binding domain (RBD) antigens occurred as early as neutralizing antibodies were detected by the ppNT and earlier than antibodies were detected by the inactivated MERS-CoV and N-terminal domain (NTD) ELISAs. Antibodies detected by the NP ELISA occurred last. Strong correlations were found between the S1, RBD and NP ELISAs and the inactivated MERS-CoV ELISA. The S and RBD ELISAs were highly correlated with the commercial S1 ELISA. The S ELISA strongly correlated with the ppNT, although the MERS-CoV, S1, NTD and RBD ELISAs were also significantly correlated with the ppNT (P<0.001).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recombinant Receptor-Binding Domains of Multiple Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses (MERS-CoVs) Induce Cross-Neutralizing Antibodies against Divergent Human and Camel MERS-CoVs and Antibody Escape Mutants.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01651-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01651-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795425 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a diagnostic system for detection of specific antibodies and antigens against Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.Microbiol Immunol. 2018 Sep;62(9):574-584. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12643. Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30117617 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Nanobody Targeting Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Receptor-Binding Domain Has Potent Cross-Neutralizing Activity and Protective Efficacy against MERS-CoV.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00837-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00837-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29950421 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for a MERS-CoV spike vaccine.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018 Aug;17(8):677-686. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2018.1506702. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2018. PMID: 30058403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies as Promising Therapeutics against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection.Viruses. 2018 Nov 30;10(12):680. doi: 10.3390/v10120680. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30513619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in Nonhuman Primates.N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 15;383(16):1544-1555. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024671. Epub 2020 Jul 28. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32722908 Free PMC article.
-
A novel luciferase immunosorbent assay performs better than a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect MERS-CoV specific IgG in humans and animals.Biosaf Health. 2019 Dec;1(3):134-143. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2019.12.006. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Biosaf Health. 2019. PMID: 32501446 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput inhibition assay to study MERS-CoV antibody interactions using image cytometry.J Virol Methods. 2019 Mar;265:77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.11.009. Epub 2018 Nov 20. J Virol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30468747 Free PMC article.
-
The Characterization of Disease Severity Associated IgG Subclasses Response in COVID-19 Patients.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 4;12:632814. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.632814. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33763078 Free PMC article.
-
Managing Preterm Infants Born to COVID-19 Mothers: Evidence from a Retrospective Cohort Study in Wuhan, China.Neonatology. 2020;117(5):592-598. doi: 10.1159/000509141. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Neonatology. 2020. PMID: 32799197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – Saudi Arabia, Disease Outbreak News, 23 March 2016. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO. 2016. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/don/23-march-2016-mers-saudi-arabia/en/ (accessed 12 April 2016).
-
- Park SW, Perera RA, Choe PG et al. Comparison of serological assays in human Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-coronavirus infection. Euro Surveill 2015; 20: 41. - PubMed
-
- Drosten C, Meyer B, Müller MA et al. Transmission of MERS-coronavirus in household contacts. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: 828–835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
