Personalized medicine in rheumatology
- PMID: 27826172
- PMCID: PMC5090026
- DOI: 10.5114/reum.2016.62472
Personalized medicine in rheumatology
Abstract
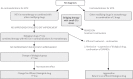
In the era of the 21st century, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is still poorly characterized. Rheumatoid arthritis is a common but heterogeneous disease, not only in the course and clinical symptoms, but also in the clinical response to treatment. Now it is known that early, correct diagnosis and starting treatment with disease-modifying drugs (DMARDs), of which methotrexate (MTX) remains the gold standard in the treatment of RA, is crucial in order to prevent joint destruction, functional disability and an unfavourable disease outcome. Early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is significant in so much as the primary treatment can be started better. Pharmacogenetic and pharmacogenomic studies, which help determine the genetic profile of individual patients, may bring us closer to personalized medicine. Further studies on RA should allow for the identification of disease-specific genes at the stage when their tolerance by the organism is still preserved (before auto-aggression develops).
Keywords: biomarkers; genetic test; personalized medicine; rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Chmara E. Medycyna spersonalizowana. Farmacja Współczesna. 2011;4:133–135.
-
- Spear BB, Heath-Chiozzi M, Huff J. Clinical application of pharmacogenetics. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7:201–204. - PubMed
-
- Ginsburg GS, McCarthy JJ. Personalized medicine: revolutionizing drug Discovery and patient care. Trends in Biotechnology. 2001;19:491–496. - PubMed
-
- Hamburg MA, Collins FS. The path to Personalized Medicine. N Engl J Med. 2010;10:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Ruano G. Quo Vadis personalized medicine? Personalized Med. 2004;1:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources