Established cell surface markers efficiently isolate highly overlapping populations of skeletal muscle satellite cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- PMID: 27826411
- PMCID: PMC5100091
- DOI: 10.1186/s13395-016-0106-6
Established cell surface markers efficiently isolate highly overlapping populations of skeletal muscle satellite cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting
Abstract
Background: Fluorescent-activated cell sorting (FACS) has enabled the direct isolation of highly enriched skeletal muscle stem cell, or satellite cell, populations from postnatal tissue. Several distinct surface marker panels containing different positively selecting surface antigens have been used to distinguish muscle satellite cells from other non-myogenic cell types. Because functional and transcriptional heterogeneity is known to exist within the satellite cell population, a direct comparison of results obtained in different laboratories has been complicated by a lack of clarity as to whether commonly utilized surface marker combinations select for distinct or overlapping subsets of the satellite cell pool. This study therefore sought to evaluate phenotypic and functional overlap among popular satellite cell sorting paradigms.
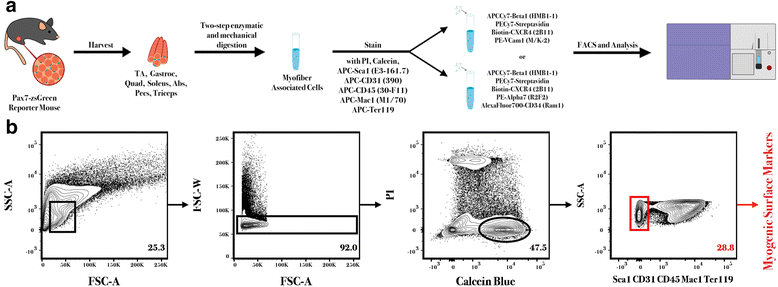
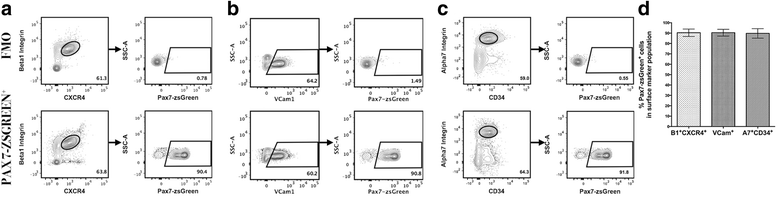
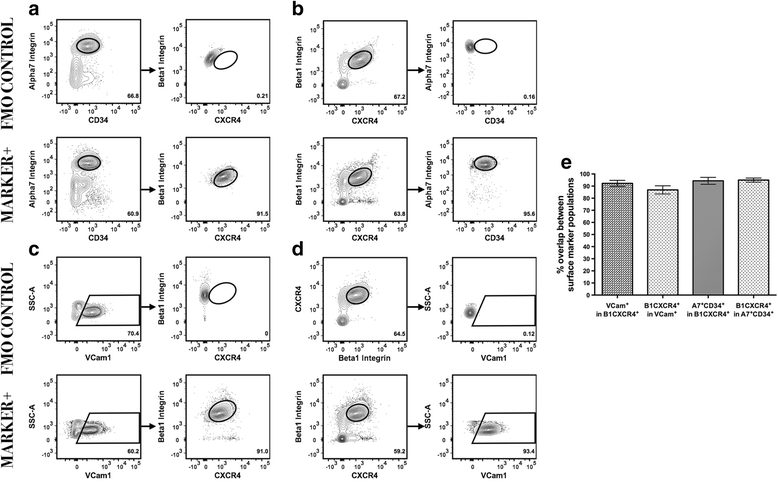
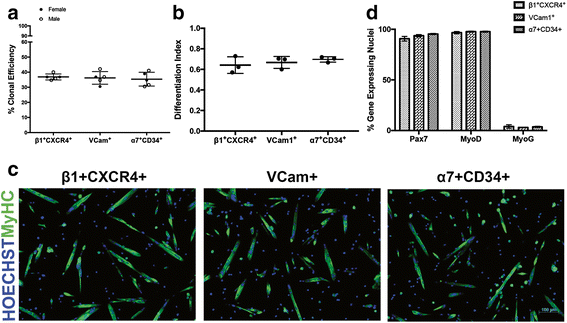
Methods: Utilizing a transgenic Pax7-zsGreen reporter mouse, we compared the overlap between the fluorescent signal of canonical paired homeobox protein 7 (Pax7) expressing satellite cells to cells identified by combinations of surface markers previously published for satellite cells isolation. We designed two panels for mouse skeletal muscle analysis, each composed of markers that exclude hematopoietic and stromal cells (CD45, CD11b, Ter119, CD31, and Sca1), combined with previously published antibody clones recognizing surface markers present on satellite cells (β1-integrin/CXCR4, α7-integrin/CD34, and Vcam1). Cell populations were comparatively analyzed by flow cytometry and FACS sorted for functional assessment of myogenic activity.
Results: Consistent with prior reports, each of the commonly used surface marker schemes evaluated here identified a highly enriched satellite cell population, with 89-90 % positivity for Pax7 expression based on zsGreen fluorescence. Distinct surface marker panels were also equivalent in their ability to identify the majority of the satellite cell pool, with 90-93 % of all Pax7-zsGreen positive cells marked by each of the surface marker schemes. The direct comparison among surface marker schemes validated their selection for highly overlapping subsets of cells. Functional analysis in vitro showed no differences in the abilities of cells sorted by these different methods to grow in culture and differentiate.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the equivalency of several previously published and widely utilized surface marker schemes for isolating a highly purified and myogenically active population of satellite cells from the mouse skeletal muscle, which should facilitate cross-comparison of data across laboratories.
Keywords: Fluorescence-activated cell sorting; Satellite cells; Surface marker.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prospective isolation of skeletal muscle stem cells with a Pax7 reporter.Stem Cells. 2008 Dec;26(12):3194-204. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-1017. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18802040 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of progenitors that exhibit myogenic/osteogenic bipotency in vitro by fluorescence-activated cell sorting from human fetal muscle.Stem Cell Reports. 2014 Jan 14;2(1):92-106. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2013.12.006. eCollection 2014 Jan 14. Stem Cell Reports. 2014. PMID: 24678452 Free PMC article.
-
A robust Pax7EGFP mouse that enables the visualization of dynamic behaviors of muscle stem cells.Skelet Muscle. 2018 Aug 24;8(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13395-018-0169-7. Skelet Muscle. 2018. PMID: 30139374 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the transcriptional signature of skeletal muscle stem cells.J Anim Sci. 2008 Apr;86(14 Suppl):E207-16. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0473. Epub 2007 Sep 18. J Anim Sci. 2008. PMID: 17878281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular regulation of muscle stem cell function.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008;73:323-31. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2008.73.064. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008. PMID: 19329572 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond the bulk: overview and novel insights into the dynamics of muscle satellite cells during muscle regeneration.Inflamm Regen. 2024 Sep 26;44(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s41232-024-00354-1. Inflamm Regen. 2024. PMID: 39327631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Interrogation of Skeletal Muscle Samples for Informative Quantitative Data.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2021;8(s2):S257-S269. doi: 10.3233/JND-210736. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2021. PMID: 34511511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOS licenses early events in stem cell activation driving skeletal muscle regeneration.Cell Rep. 2021 Jan 26;34(4):108656. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108656. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33503437 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of radiation exposure, hindlimb unloading, and recovery on murine skeletal muscle cell telomere length.NPJ Microgravity. 2023 Sep 15;9(1):76. doi: 10.1038/s41526-023-00303-1. NPJ Microgravity. 2023. PMID: 37714858 Free PMC article.
-
A novel protocol for the direct isolation of a highly pure and regenerative population of satellite stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jun 24;122(25):e2426081122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2426081122. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40531869
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

