Recurrence Rates and Risk Factors for Primary Giant Cell Tumors around the Knee: A Multicentre Retrospective Study in China
- PMID: 27827384
- PMCID: PMC5101496
- DOI: 10.1038/srep36332
Recurrence Rates and Risk Factors for Primary Giant Cell Tumors around the Knee: A Multicentre Retrospective Study in China
Abstract
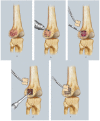
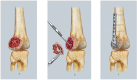
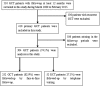
Giant cell tumors of the bone (GCTBs) are commonly diagnosed in Asian populations, usually around the knee. Herein, we aimed to determine the clinical characteristics, local recurrence rates, and relevant risk factors of primary GCTB around the knee. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were used to identify the risk factors for local recurrence. Four hundred ten patients with primary GCTB around the knee, treated between March 2000 and June 2014, were recruited from 7 institutions in China. The overall local recurrence rate was 23.4%, but was higher in patients aged 20-39 years (28.5%; P = 0.039). The local recurrence rate was the highest in patients treated with intralesional curettage (53.4%), and the lowest in those treated with resection (4.9%). We found a higher risk of tumor recurrence in the proximal fibula compared to the distal femur (hazard ratio: 28.52, 95% confidence interval: 5.88-138.39; P < 0.0001), and in patients treated with curettage compared to those treated with resection (hazard ratio: 12.07, 95% confidence interval: 4.99-29.18; P < 0.0001). Thus, the tumor location must be considered when selecting the optimal surgical treatment approach to reduce the risk of local recurrence and preserve joint function, especially in young patients.
Figures



References
-
- Campanacci M. In Bone and soft tissue tumors: clinical features, imaging, pathology and treatment 2nd edn (Springer, 1999).
-
- Hu Y., Chen Y. & Lun D. The establishing and verification of clinical scoring system for giant cell tumor. Chinse Journal of Orthopadics . 3l, 105–112 (2011).
-
- Tureotte R. E. Giant cell tumor of bone. Onhop Clin Noah Am . 37, 35–51 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

