Altered Translational Control of Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein on Myelin Proteins in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
- PMID: 27829268
- PMCID: PMC5424632
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.042
Altered Translational Control of Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein on Myelin Proteins in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Abstract
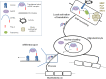
Myelin is a specialized structure of the nervous system that both enhances electrical conductance and insulates neurons from external risk factors. In the central nervous system, polarized oligodendrocytes form myelin by wrapping processes in a spiral pattern around neuronal axons through myelin-related gene regulation. Since these events occur at a distance from the cell body, post-transcriptional control of gene expression has strategic advantage to fine-tune the overall regulation of protein contents in situ. Therefore, many research interests have been focused to identify RNA binding proteins and their regulatory mechanism in myelinating compartments. Fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) is one such RNA binding protein, regulating its target expression by translational control. Although the majority of works on FMRP have been performed in neurons, it is also found in the developing or mature glial cells including oligodendrocytes, where its function is not well understood. Here, we will review evidences suggesting abnormal translational regulation of myelin proteins with accompanying white matter problem and neurological deficits in fragile X syndrome, which can have wider mechanistic and pathological implication in many other neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Fragile X mental retardation protein; Myelin; Oligodendrocyte; Translational control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of myelin formation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Aug;1779(8):486-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.06.003. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18590840 Review.
-
Expression of fragile X mental retardation-1 gene with nuclear export signal mutation changes the expression profiling of mouse cerebella immortal neuronal cell.Proteomics. 2005 Oct;5(15):3979-90. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200401252. Proteomics. 2005. PMID: 16130171
-
Delayed myelination in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Oct 1;22(19):3920-30. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt246. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23740941
-
Expression of fragile X mental retardation protein in neurons and glia of the developing and adult mouse brain.Brain Res. 2015 Jan 30;1596:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.023. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25446451
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein: A paradigm for translational control by RNA-binding proteins.Biochimie. 2015 Jul;114:147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25701550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myelination Deficits in the Auditory Brainstem of a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 11;15:772943. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.772943. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34858133 Free PMC article.
-
Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Spectroscopy (CARS) Application for Imaging Myelination in Brain Slices.J Vis Exp. 2022 Jul 22;(185):10.3791/64013. doi: 10.3791/64013. J Vis Exp. 2022. PMID: 35938838 Free PMC article.
-
Cyfip1 haploinsufficient rats show white matter changes, myelin thinning, abnormal oligodendrocytes and behavioural inflexibility.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 1;10(1):3455. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11119-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31371763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbarese E, Koppel DE, Deutscher MP, Smith CL, Ainger K, Morgan F, Carson JH. Protein translation components are colocalized in granules in oligodendrocytes. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:2781–2790. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

