Oxidative Stress during HIV Infection: Mechanisms and Consequences
- PMID: 27829986
- PMCID: PMC5088339
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8910396
Oxidative Stress during HIV Infection: Mechanisms and Consequences
Abstract
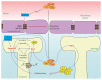
It is generally acknowledged that reactive oxygen species (ROS) play crucial roles in a variety of natural processes in cells. If increased to levels which cannot be neutralized by the defense mechanisms, they damage biological molecules, alter their functions, and also act as signaling molecules thus generating a spectrum of pathologies. In this review, we summarize current data on oxidative stress markers associated with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infection, analyze mechanisms by which this virus triggers massive ROS production, and describe the status of various defense mechanisms of the infected host cell. In addition, we have scrutinized scarce data on the effect of ROS on HIV-1 replication. Finally, we present current state of knowledge on the redox alterations as crucial factors of HIV-1 pathogenicity, such as neurotoxicity and dementia, exhaustion of CD4+/CD8+ T-cells, predisposition to lung infections, and certain side effects of the antiretroviral therapy, and compare them to the pathologies associated with the nitrosative stress.
Figures

References
-
- Gutowski M., Kowalczyk S. A study of free radical chemistry: their role and pathophysiological significance. Acta Biochimica Polonica. 2013;60(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Augusto O., Miyamoto S. Oxygen radicals and related species. In: Pantopoulos K., Schipper H. M., editors. Principles of Free Radical Biomedicine. Nova Science Publishers; 2011. pp. 1–23.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

