PLK1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric carcinoma cells
- PMID: 27830001
- PMCID: PMC5095310
PLK1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric carcinoma cells
Abstract
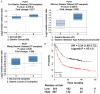
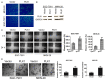
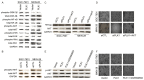
Cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is the crucial event for cancer progression and plays a vital role in the metastasis of cancer cells. Activation of Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) signaling has been implicated as the critical event in several tumor metastasis and EMT, however, whether PLK1 participates in gastric carcinoma metastasis and EMT still remains unclear. For this study, we elucidated the potential physiological function of PLK1 in the metastasis of gastric tumors, as well its distinct role in cells EMT and subsequently determined the mechanism involved in PLK1 regulated. Immunoblotting assay and Oncomine data mining analysis indicated that PLK1 expression was highly up-regulated in gastric carcinoma. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for the relationship between survival outcomes and PLK1 expression in gastric carcinoma was performed with an online Kaplan-Meier plotter (http://kmplot.com/analysis/). Over-expression of PLK1 in gastric cancer cells SGC-7901 and MKN-28 significantly promoted cells profound morphological changes and enhanced metastatic ability of tumor cells. On the contrary, silencing of PLK1 induced mesenchymal epithelial transition (MET)-like morphological and inhibited the metastatic process. Furthermore, we found that the metastatic characters promoting effects of PLK1 in gastric carcinoma was related to the activation of protein kinase B (AKT). Our mechanistic investigations revealed that AKT inhibition reversed PLK1-induced EMT, blocked gastric carcinoma cells invasiveness and metastasis. Additionally, over-expression of AKT promoted the migratory and invasion ability of the two cell lines, which was disrupted by PLK1 down-regulation. To conclude, our findings demonstrate that PLK1 accelerates the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchyme transition of gastric cancer cells through regulating the AKT pathway.
Keywords: EMT; PLK1; gastric carcinoma; metastasis.
Figures
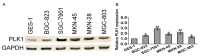


Similar articles
-
Metastasis suppressor protein 1 regulated by PTEN suppresses invasion, migration, and EMT of gastric carcinoma by inactivating PI3K/AKT signaling.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar;120(3):3447-3454. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27618. Epub 2018 Sep 23. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30246429
-
RNF8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 4;35(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0363-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27259701 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of PLK1 on proliferation, invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncol Lett. 2018 Nov;16(5):5739-5744. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9406. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30405751 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Polo-Like Kinase 1 in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2017 Sep 27;9(10):131. doi: 10.3390/cancers9100131. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28953239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collection on reports of molecules linked to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the process of treating metastasizing cancer: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jun;9(11):946. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-7002. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34350261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The anticipating value of PLK1 for diagnosis, progress and prognosis and its prospective mechanism in gastric cancer: a comprehensive investigation based on high-throughput data and immunohistochemical validation.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 30;8(54):92497-92521. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21438. eCollection 2017 Nov 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29190933 Free PMC article.
-
Active PLK1-driven metastasis is amplified by TGF-β signaling that forms a positive feedback loop in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(4):767-785. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1023-z. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31548612 Free PMC article.
-
PLK1 in cancer therapy: a comprehensive review of immunomodulatory mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 19;16:1602752. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602752. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40612941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Analyses Reveal the Multi-Omics and Prognostic Characteristics of ATP5B in Breast Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 May 28;12:652474. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.652474. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34122507 Free PMC article.
-
OCT4B1 Promoted EMT and Regulated the Self-Renewal of CSCs in CRC: Effects Associated with the Balance of miR-8064/PLK1.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019 Aug 28;15:7-20. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2019.08.004. eCollection 2019 Dec 20. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019. PMID: 31650021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kadletz L, Bigenzahn J, Thurnher D, Stanisz I, Erovic BM, Schneider S, Schmid R, Seemann R, Birner P, Heiduschka G. Evaluation of Polo-like kinase 1 as a potential therapeutic target in Merkel cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2016;38(Suppl 1):E1918–1925. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Acenero MJ, Cortes D, Gomez Del Pulgar T, Cebrian A, Estrada L, Martinez-Useros J, Celdran A, Garcia-Foncillas J, Pastor C. PLK-1 Expression is Associated with Histopathological Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy of Hepatic Metastasis of Colorectal Carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 2016;22:377–383. - PubMed
-
- Zhao CL, Ju JY, Gao W, Yu WJ, Gao ZQ, Li WT. Downregulation of PLK1 by RNAi attenuates the tumorigenicity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via promoting apoptosis and inhibiting angiogenesis. Neoplasma. 2015;62:748–755. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
