Tongxinluo modulates cytokine secretion by cardiac microvascular endothelial cells in ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 27830021
- PMCID: PMC5095330
Tongxinluo modulates cytokine secretion by cardiac microvascular endothelial cells in ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
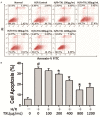
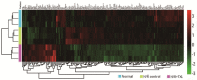
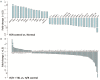
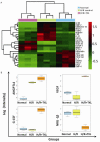
Cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (CMECs) extensively secrete cytokines during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI). Tongxinluo (TXL) has been demonstrated to preserve the function of the endothelium and myocardium against MIRI. This study was designed to identify alterations in the paracrine function of CMECs under hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) conditions and assess its modulation by TXL. CMECs were exposed to different concentrations of TXL for 30 min and then subjected to hypoxia and reoxygenation for 12 and 2 h, respectively. Apoptosis was measured to determine the optimal TXL concentration. Protein antibody arrays were used to assess changes in cytokines secreted into conditioned medium by CMECs. A Gene Ontology (GO) analysis was applied to interpret the functional implications of changes in cytokines. TXL inhibited CMEC apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner after H/R, reaching peak efficacy at a concentration of 800 μg/ml. H/R significantly altered 33 cytokines, and TXL (800 μg/ml) changed the levels of 121 different cytokines compared with the H/R group. Among these cytokines, 10 that were increased by H/R were decreased by TXL, five that were decreased by H/R were increased by TXL, and eight that were attenuated by H/R were further decreased by TXL. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 was up-regulated by H/R and was further increased by TXL. Significantly altered factors were found to be involved in cell proliferation, growth and differentiation, as well as chemotaxis and transport. TXL inhibited the apoptosis of CMECs and modulated their paracrine function in MIRI.
Keywords: Cytokine; Tongxinluo; cardiac microvascular endothelial cells; myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; paracrine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury-Modulated Proteins in Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells and the Protective Role of Tongxinluo.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1503-1518. doi: 10.1159/000470806. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28334711
-
Resveratrol regulates paracrine function of cardiac microvascular endothelial cells under hypoxia/reoxygenation condition.Pharmazie. 2022 Jun 1;77(6):179-185. doi: 10.1691/ph.2022.2370. Pharmazie. 2022. PMID: 35751162
-
Induction of autophagy by Tongxinluo through the MEK/ERK pathway protects human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;64(2):180-90. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000104. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24705173
-
Cardiomyocyte-derived small extracellular vesicles can signal eNOS activation in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells to protect against Ischemia/Reperfusion injury.Theranostics. 2020 Sep 23;10(25):11754-11774. doi: 10.7150/thno.43163. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 33052245 Free PMC article.
-
Tongxinluo attenuates reperfusion injury in diabetic hearts by angiopoietin-like 4-mediated protection of endothelial barrier integrity via PPAR-α pathway.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 18;13(6):e0198403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198403. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29912977 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical effects and mechanisms of a Chinese patent medicine, Tongxinluo capsule, as an adjuvant treatment in coronary heart disease.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 6;10(6):e27460. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27460. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38533036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tongxinluo Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Mainly via Activating Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy and Downregulating Ubiquitin-Proteasome System.Chin J Integr Med. 2021 Jul;27(7):542-550. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3166-8. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Chin J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 31227964
-
Therapeutic Angiogenesis of Chinese Herbal Medicines in Ischemic Heart Disease: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 26;9:428. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00428. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29755358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tongxinluo attenuates oxygen-glucose-serum deprivation/restoration-induced endothelial barrier breakdown via peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α/angiopoietin-like 4 pathway in high glucose-incubated human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 21;99(34):e21821. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021821. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32846824 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-128-3p by Tongxinluo Protects Human Cardiomyocytes from Ischemia/reperfusion Injury via Upregulation of p70s6k1/p-p70s6k1.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 30;8:775. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00775. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29163161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial Reperfusion Injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1121–1135. - PubMed
-
- Prasad A, Stone GW, Holmes DR, Gersh B. Reperfusion injury, microvascular dysfunction, and cardioprotection: the “dark side” of reperfusion. Circulation. 2009;120:2105–2112. - PubMed
-
- Camici PG, Crea F. Coronary microvascular dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:830–840. - PubMed
-
- Brutsaert DL. Cardiac Endothelial-Myocardial Signaling: Its Role in Cardiac Growth, Contractile Performance, and Rhythmicity. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:59–115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
