Determination of Levetiracetam in Human Plasma by Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 27830105
- PMCID: PMC5086507
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/5976324
Determination of Levetiracetam in Human Plasma by Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
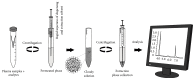
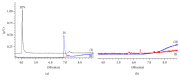
Levetiracetam (LEV) is an antiepileptic drug that is clinically effective in generalized and partial epilepsy syndromes. The use of this drug has been increasing in clinical practice and intra- or -interindividual variability has been exhibited for special population. For this reason, bioanalytical methods are required for drug monitoring in biological matrices. So this work presents a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (DLLME-GC-MS) for LEV quantification in human plasma. However, due to the matrix complexity a previous purification step is required. Unlike other pretreatment techniques presented in the literature, for the first time, a procedure employing ultrafiltration tubes Amicon® (10 kDa porous size) without organic solvent consumption was developed. GC-MS analyses were carried out using a linear temperature program, capillary fused silica column, and helium as the carrier gas. DLLME optimized parameters were type and volume of extraction and dispersing solvents, salt addition, and vortex agitation time. Under chosen parameters (extraction solvent: chloroform, 130 μL; dispersing solvent: isopropyl alcohol, 400 μL; no salt addition and no vortex agitation time), the method was completely validated and all parameters were in agreement with the literature recommendations. LEV was quantified in patient's plasma sample using less than 550 μL of organic solvent.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Green aspects, developments and perspectives of liquid phase microextraction techniques.Talanta. 2014 Feb;119:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.10.050. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Talanta. 2014. PMID: 24401382 Review.
-
Low-density solvent-based vortex-assisted surfactant-enhanced-emulsification liquid-liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the fast determination of phthalate esters in bottled water.J Chromatogr A. 2013 Jan 25;1274:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.12.017. Epub 2012 Dec 19. J Chromatogr A. 2013. PMID: 23290358
-
Fast, sensitive and reliable multi-residue method for routine determination of 34 pesticides from various chemical groups in water samples by using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Feb;410(5):1533-1550. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0798-4. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29256082
-
Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction, an effective tool for the determination of synthetic cannabinoids in oral fluid by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Anal. 2021 Jun;11(3):292-298. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Nov 19. J Pharm Anal. 2021. PMID: 34277117 Free PMC article.
-
Solvent-terminated dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction: a tutorial.Anal Chim Acta. 2018 Aug 3;1016:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Anal Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29534799 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring of levetiracetam: Method validation using high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detector technique and usefulness in patient care setting.J Postgrad Med. 2023 Apr-Jun;69(2):72-80. doi: 10.4103/jpgm.jpgm_467_21. J Postgrad Med. 2023. PMID: 36255019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shah J. S., Vidyasagar G., Barot H. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for estimation of levetiracetam in pharmaceutical formulation and application to pharmacokinetic study. Der Pharmacia Sinica. 2012;3(5):576–589.
-
- French J. A., Tonner F. Levetiracetam. In: Shorvon S., Perucca E., Engel J., editors. The Treatment of Epilepsy. 3rd. chapter 44. 2009. pp. 559–573.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

