Effect of high fat diet on pulmonary expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein and its downstream targets
- PMID: 27830194
- PMCID: PMC5094380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00182
Effect of high fat diet on pulmonary expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein and its downstream targets
Abstract
Aims: Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is involved in lung development and surfactant production. The latter one requires a paracrine interaction between type II alveolar cells and lipofibroblasts in which leptin triggers PTHrP-induced effects. Whether increased plasma leptin levels, as they occur in high fat diet, modify the expression of PTHrP remains unclear. Furthermore, the effect of high fat diet under conditions of forced pulmonary remodelling such as response to post myocardial infarction remains to be defined.
Materials and methods: C57 bl/6 mice were randomized to either normal diet or high fat diet at an age of 6 weeks. Seven months later, the mice were euthanized and the lung was removed and frozen in fluid nitrogen until use. Samples were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR and western blot. Leptin deficient mice were used to investigate the effect of leptin on pulmonary expression of PTHrP more directly. A subgroup of mice with and without high fat diet underwent in vivo ischemia (45 min) and reperfusion (4 weeks). Finally, experiments were repeated with prolonged high-fat diet.
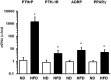
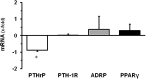
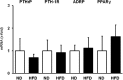
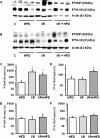
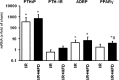
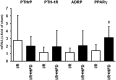
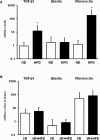
Key findings: High fat diet increased plasma leptin levels by 30.4% and the pulmonary mRNA expression of PTHrP (1,447-fold), PTH-1 receptor (4.21-fold), and PTHrP-downstream targets ADRP (7.54-fold) and PPARγ (5.27-fold). Pulmonary PTHrP expression was reduced in leptin deficient mice by 88% indicating leptin dependent regulation. High fat diet further improved changes in pulmonary adaptation caused by ischemia/reperfusion (1.48-fold increased PTH-1 receptor protein expression). These effects were lost during prolonged high fat diet.
Significance: This study established that physiological regulation of leptin plasma levels by high fat diet affects the pulmonary PTHrP expression and of PTHrP downstream targets. Modification of pulmonary expression of PTH-1 receptors by high fat diet after myocardial infarction suggests that the identified interaction may participate in the obesity paradox.
Keywords: Medicine; Physiology.
Figures
References
-
- Cantor J.O., Keller S., Mandl I., Turino G.M. Increased synthesis of elastin in amiodarone-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1987;109:480–485. - PubMed
-
- Doi T., Lukosiute A., Ruttenstock E., Dingemann J., Puri P. Distribution of parathyroid hormone-related protein signaling in the nitrofen-induced hypopastic lung. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2010;26:45–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

