Glutamine for the treatment of vincristine-induced neuropathy in children and adolescents with cancer
- PMID: 27830395
- PMCID: PMC5598352
- DOI: 10.1007/s00520-016-3441-6
Glutamine for the treatment of vincristine-induced neuropathy in children and adolescents with cancer
Abstract
Background: Vincristine is an integral treatment component of many childhood tumors with potentially dose-limiting sensory and/or motor neuropathy. Results from a pilot study on the incidence of vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy (VIPN) as well as the efficacy and safety of glutamine in reducing signs and symptoms of VIPN in children with cancer are presented.
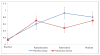
Methods: Fifty-six patients between the ages of 5-21 with newly diagnosed leukemia, lymphoma, extracranial solid tumor or medulloblastoma and expected to receive a minimum cumulative dose of 6 mg/m2 of vincristine over a 30-week period were eligible. Patients' neurological functioning was monitored every 3 weeks using clinical history, exam, and assessment of motor functioning. Upon identification of neuropathy, patients were randomized to either glutamine (6 g/m2 per dose twice daily, maximum 10 g/dose) or placebo for a 3-week period followed by 3-week wash out period (Time 3).
Results: Forty-nine patients were fully evaluable and 100 % developed neuropathy per study definitions. No significant differences in demographics or side effects were noted between the randomized groups. The distribution of sensory neuropathy scores between the two groups was statistically significant after the intervention (p = 0.022). Children receiving glutamine also rated their quality of life (QoL) as 8.42 points higher on the PedsQL total score than those receiving placebo (p = 0.031).
Conclusions: Glutamine supplementation is well tolerated and associated with improvements in sensory function and self-reported overall quality of life. Future studies are warranted to confirm the efficacy of glutamine for the treatment of vincristine-related sensory neuropathy in pediatric cancer patients.
Keywords: Glutamine; Integrative medicine; Neuropathy; Quality of life; Supportive care.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gidding CEM, Kellie SJ, Kamps WA, de Graaf SSN. Vincristine revisited. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1999;29:267–287. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MA, Wilson L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:253–265. - PubMed
-
- Legha SS. Vincristine neurotoxicity. Pathophysiology and management. Medical toxicology. 1986;1:421–427. - PubMed
-
- Smith EML, Cohen JA, Pett MA, Beck SL. The reliability and validity of a modified Total neuropathy score-reduced and neuropathic pain severity items when used to measure chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving Taxanes and Platinums. Cancer Nurs. 2010;33:173–183. - PubMed
-
- Gilchrist LS, Tanner L. The pediatric-modified total neuropathy score: a reliable and valid measure of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in children with non-CNS cancers. Support Care Cancer: Off J Multinatl Assoc Support Care Cancer. 2013;21:847–856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical