Synthetic genome readers target clustered binding sites across diverse chromatin states
- PMID: 27830652
- PMCID: PMC5127382
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1604847113
Synthetic genome readers target clustered binding sites across diverse chromatin states
Abstract
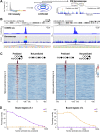
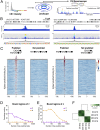
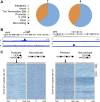
Targeting the genome with sequence-specific DNA-binding molecules is a major goal at the interface of chemistry, biology, and precision medicine. Polyamides, composed of N-methylpyrrole and N-methylimidazole monomers, are a class of synthetic molecules that can be rationally designed to "read" specific DNA sequences. However, the impact of different chromatin states on polyamide binding in live cells remains an unresolved question that impedes their deployment in vivo. Here, we use cross-linking of small molecules to isolate chromatin coupled to sequencing to map the binding of two bioactive and structurally distinct polyamides to genomes directly within live H1 human embryonic stem cells. This genome-wide view from live cells reveals that polyamide-based synthetic genome readers bind cognate sites that span a range of binding affinities. Polyamides can access cognate sites within repressive heterochromatin. The occupancy patterns suggest that polyamides could be harnessed to target loci within regions of the genome that are inaccessible to other DNA-targeting molecules.
Keywords: COSMIC; chemical genomics; genome targeting; molecular recognition; polyamide.
Conflict of interest statement
A.Z.A. is the sole member of VistaMotif, LLC and founder of the nonprofit WINStep Forward.
Figures


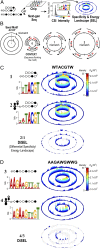
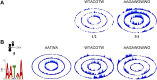
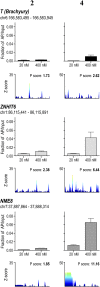
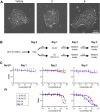

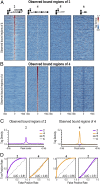
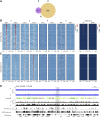
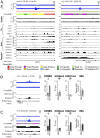
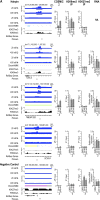


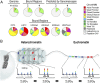
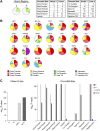
References
-
- Wang D, Lippard SJ. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(4):307–320. - PubMed
-
- Hurley LH. DNA and its associated processes as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(3):188–200. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez R, Miller KM. Unravelling the genomic targets of small molecules using high-throughput sequencing. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(12):783–796. - PubMed
-
- Dervan PB. Molecular recognition of DNA by small molecules. Bioorg Med Chem. 2001;9(9):2215–2235. - PubMed
-
- Dickinson LA, et al. Inhibition of Ets-1 DNA binding and ternary complex formation between Ets-1, NF-kappaB, and DNA by a designed DNA-binding ligand. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(18):12765–12773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

