Sensing of HSV-1 by the cGAS-STING pathway in microglia orchestrates antiviral defence in the CNS
- PMID: 27830700
- PMCID: PMC5109551
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13348
Sensing of HSV-1 by the cGAS-STING pathway in microglia orchestrates antiviral defence in the CNS
Abstract
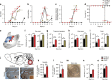
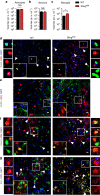
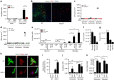
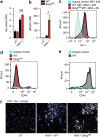
Herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE) is the most common form of acute viral encephalitis in industrialized countries. Type I interferon (IFN) is important for control of herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) in the central nervous system (CNS). Here we show that microglia are the main source of HSV-induced type I IFN expression in CNS cells and these cytokines are induced in a cGAS-STING-dependent manner. Consistently, mice defective in cGAS or STING are highly susceptible to acute HSE. Although STING is redundant for cell-autonomous antiviral resistance in astrocytes and neurons, viral replication is strongly increased in neurons in STING-deficient mice. Interestingly, HSV-infected microglia confer STING-dependent antiviral activities in neurons and prime type I IFN production in astrocytes through the TLR3 pathway. Thus, sensing of HSV-1 infection in the CNS by microglia through the cGAS-STING pathway orchestrates an antiviral program that includes type I IFNs and immune-priming of other cell types.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microglia Activate Early Antiviral Responses upon Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Entry into the Brain to Counteract Development of Encephalitis-Like Disease in Mice.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0131121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01311-21. Epub 2022 Jan 19. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35045263 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Abrogates the cGAS/STING-Mediated Cytosolic DNA-Sensing Pathway via Its Virion Host Shutoff Protein, UL41.J Virol. 2017 Feb 28;91(6):e02414-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02414-16. Print 2017 Mar 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28077645 Free PMC article.
-
The intracellular DNA sensors cGAS and IFI16 do not mediate effective antiviral immune responses to HSV-1 in human microglial cells.J Neurovirol. 2020 Aug;26(4):544-555. doi: 10.1007/s13365-020-00852-1. Epub 2020 Jun 2. J Neurovirol. 2020. PMID: 32488842 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and spatial mechanisms governing STING signalling.FEBS J. 2021 Oct;288(19):5504-5529. doi: 10.1111/febs.15640. Epub 2020 Dec 11. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33237620 Review.
-
Roles of HSV-1 infection-induced microglial immune responses in CNS diseases: friends or foes?Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019 Sep-Nov;45(5-6):581-594. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2019.1660615. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31512533 Review.
Cited by
-
cGAS-STING signalling regulates microglial chemotaxis in genome instability.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1188-1206. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1184. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38084916 Free PMC article.
-
An Early Microglial Response Is Needed To Efficiently Control Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis.J Virol. 2020 Nov 9;94(23):e01428-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01428-20. Print 2020 Nov 9. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32938766 Free PMC article.
-
When herpes simplex virus encephalitis meets antiviral innate immunity.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 20;14:1118236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1118236. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36742325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of STING signaling in central nervous system infection and neuroinflammatory disease.WIREs Mech Dis. 2023 May-Jun;15(3):e1597. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1597. Epub 2023 Jan 12. WIREs Mech Dis. 2023. PMID: 36632700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exaggerated levels of some specific TLRs, cytokines and chemokines in Japanese encephalitis infected BV2 and neuro 2A cell lines associated with worst outcome.Virol J. 2023 Jan 27;20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-01966-8. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 36707891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roizman B., Knipe D. M. & Whitley R. J. Herpes simplex viruses in Fields Virology. eds Knipe D. M., Howley P. M. 2501–2602Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins (2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

