A dynamic in vivo-like organotypic blood-brain barrier model to probe metastatic brain tumors
- PMID: 27830712
- PMCID: PMC5103210
- DOI: 10.1038/srep36670
A dynamic in vivo-like organotypic blood-brain barrier model to probe metastatic brain tumors
Abstract
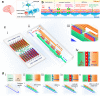
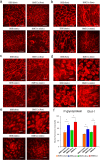
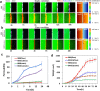
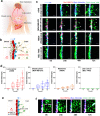
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) restricts the uptake of many neuro-therapeutic molecules, presenting a formidable hurdle to drug development in brain diseases. We proposed a new and dynamic in vivo-like three-dimensional microfluidic system that replicates the key structural, functional and mechanical properties of the blood-brain barrier in vivo. Multiple factors in this system work synergistically to accentuate BBB-specific attributes-permitting the analysis of complex organ-level responses in both normal and pathological microenvironments in brain tumors. The complex BBB microenvironment is reproduced in this system via physical cell-cell interaction, vascular mechanical cues and cell migration. This model possesses the unique capability to examine brain metastasis of human lung, breast and melanoma cells and their therapeutic responses to chemotherapy. The results suggest that the interactions between cancer cells and astrocytes in BBB microenvironment might affect the ability of malignant brain tumors to traverse between brain and vascular compartments. Furthermore, quantification of spatially resolved barrier functions exists within a single assay, providing a versatile and valuable platform for pharmaceutical development, drug testing and neuroscientific research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood-brain barrier interfaces and brain tumors.Arch Pharm Res. 2006 Apr;29(4):265-75. doi: 10.1007/BF02968569. Arch Pharm Res. 2006. PMID: 16681030 Review.
-
The role of the organ microenvironment in brain metastasis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2011 Apr;21(2):107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.12.009. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011. PMID: 21167939 Review.
-
The Biology of Brain Metastasis: Challenges for Therapy.Cancer J. 2015 Jul-Aug;21(4):284-93. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000126. Cancer J. 2015. PMID: 26222080 Review.
-
Thin platelet-like COF nanocomposites for blood brain barrier transport and inhibition of brain metastasis from renal cancer.J Mater Chem B. 2020 May 27;8(20):4475-4488. doi: 10.1039/d0tb00724b. J Mater Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32365151
-
The role of claudin-5 in blood-brain barrier (BBB) and brain metastases (review).Mol Med Rep. 2014 Mar;9(3):779-85. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2013.1875. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24366267 Review.
Cited by
-
State of the Art Modelling of the Breast Cancer Metastatic Microenvironment: Where Are We?J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2024 Jul 16;29(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s10911-024-09567-z. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 39012440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-on-a-chip: A history of development and future perspective.Biomicrofluidics. 2019 Oct 8;13(5):051301. doi: 10.1063/1.5120555. eCollection 2019 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2019. PMID: 31616534 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing cancer extravasation: from mechanistic studies to drug development.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021 Mar;40(1):71-88. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09942-2. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021. PMID: 33156478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue Response to Neural Implants: The Use of Model Systems Toward New Design Solutions of Implantable Microelectrodes.Front Neurosci. 2019 Jul 5;13:689. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00689. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31333407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Open multi-culture platform for simple and flexible study of multi-cell type interactions.Lab Chip. 2018 Oct 9;18(20):3184-3195. doi: 10.1039/c8lc00560e. Lab Chip. 2018. PMID: 30204194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubin L. L. & Staddon J. M. The cell biology of the blood-brain barrier. Annu Rev Neurosci. 22, 11–28 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Abbott N. J., Ronnback L. & Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 7, 41–53 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm I., Fazakas C. & Krizbai I. A. In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier. Acta Neurobiol Exp. 71, 113–128 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Zipser B. D. et al.. Microvascular injury and blood-brain barrier leakage in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of aging 28, 977–986 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Kahles T. et al.. NADPH oxidase plays a central role in blood-brain barrier damage in experimental stroke. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 38, 3000–3006 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

