Development of a Model of Pediatric Lung Failure Pathophysiology
- PMID: 27832003
- PMCID: PMC5325792
- DOI: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000000463
Development of a Model of Pediatric Lung Failure Pathophysiology
Abstract
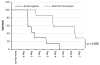
A pediatric artificial lung (PAL) is under development as a bridge to transplantation or lung remodeling for children with end-stage lung failure (ESLF). To evaluate the efficiency of a PAL, a disease model mimicking the physiologic derangements of pediatric ESLF is needed. Our previous right pulmonary artery (rPA) ligation model (rPA-LM) achieved that goal, but caused immediate mortality in nearly half of the animals. In this study, we evaluated a new technique of gradual postoperative right pulmonary artery occlusion using a Rummel tourniquet (rPA-RT) in seven (25-40 kg) sheep. This technique created a stable model of ESLF pathophysiology, characterized by high alveolar dead space (58.0% ± 3.8%), pulmonary hypertension (38.4 ± 2.2 mm Hg), tachypnea (79 ± 20 breaths per minute), and intermittent supplemental oxygen requirement. This improvement to our technique provides the necessary physiologic derangements for testing a PAL, whereas avoiding the problem of high immediate perioperative mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
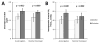


Similar articles
-
A Model of Pediatric End-Stage Lung Failure in Small Lambs <20 kg.ASAIO J. 2020 May;66(5):572-579. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001017. ASAIO J. 2020. PMID: 31294720 Free PMC article.
-
The Implantable Pediatric Artificial Lung: Interim Report on the Development of an End-Stage Lung Failure Model.ASAIO J. 2015 Jul-Aug;61(4):453-8. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000000230. ASAIO J. 2015. PMID: 25905495 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Artificial Lung: A Low-Resistance Pumpless Artificial Lung Alleviates an Acute Lamb Model of Increased Right Ventricle Afterload.ASAIO J. 2017 Mar/Apr;63(2):223-228. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000000481. ASAIO J. 2017. PMID: 27861431 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an implantable artificial lung: challenges and progress.ASAIO J. 2001 Jul-Aug;47(4):316-20. doi: 10.1097/00002480-200107000-00003. ASAIO J. 2001. PMID: 11482477 Review.
-
Artificial lung: current perspectives.Minerva Chir. 2008 Oct;63(5):363-72. Minerva Chir. 2008. PMID: 18923347 Review.
Cited by
-
A Model of Pediatric End-Stage Lung Failure in Small Lambs <20 kg.ASAIO J. 2020 May;66(5):572-579. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001017. ASAIO J. 2020. PMID: 31294720 Free PMC article.
-
The horizon of pediatric cardiac critical care.Front Pediatr. 2022 Sep 16;10:863868. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.863868. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36186624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valapour M, Paulson K, Smith J, et al. Optn/srtr 2011 annual data report: Lung. American Journal of Transplantation. 2013;13:149–177. - PubMed
-
- Turner DA, Cheifetz IM, Rehder KJ, et al. Active rehabilitation and physical therapy during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation while awaiting lung transplantation: A practical approach. Critical care medicine. 2011;39:2593–2598. - PubMed
-
- Dipchand AI, Kirk R, Edwards LB, et al. The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: Sixteenth official pediatric heart transplantation report—2013; focus theme: Age. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2013;32:979–988. - PubMed
-
- Kinsella JP, Greenough A, Abman SH. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The Lancet. 2006;367:1421–1431. - PubMed
-
- Dishop MK. Paediatric interstitial lung disease: Classification and definitions. Paediatric respiratory reviews. 2011;12:230–237. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

