Elevated Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Humans with Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 27832059
- PMCID: PMC5104316
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164351
Elevated Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Humans with Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
Background: The metabolic regulator Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) is highly expressed in the acinar pancreas, but its role in pancreatic function is obscure. It appears to play a protective role in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. The aim of this study was to define an association between FGF21 and the course and resolution of acute pancreatitis in humans.
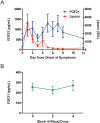
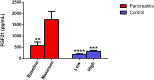
Methods and principal findings: Twenty five subjects with acute pancreatitis admitted from May to September 2012 to the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) were analyzed. Serial serum samples were collected throughout hospitalization and analyzed for FGF21 levels by ELISA. Twenty healthy subjects sampled three times over a four week period were used as controls. We found that, in patients with pancreatitis, serum FGF21 rises significantly and peaks four to six days after the maximum lipase level, before slowly declining. Maximum FGF21 levels were significantly greater than baseline levels for acute pancreatitis subjects (1733 vs. 638 pg/mL, P = 0.003). This maximum value was significantly greater than the highest value observed for our control subjects (1733 vs. 322 pg/mL, P = 0.0002). The ratio of active to total FGF21 did not change during the course of the disease (42.5% vs. 44.4%, P = 0.58). Fold increases in FGF21 were significantly greater in acute pancreatitis subjects than the fold difference seen in healthy subjects (4.7 vs. 2.0, P = 0.01). Higher fold changes were also seen in severe compared to mild pancreatitis (18.2 vs. 4.4, P = 0.01). The timing of maximum FGF21 levels correlated with day of successful return to oral intake (R2 = 0.21, P = 0.04).
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that serum FGF21 rises significantly in humans with acute pancreatitis. The pancreas may be contributing to increased FGF21 levels following injury and FGF21 may play a role in the recovery process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates acute pancreatitis via activation of the Sirt1-autophagy signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 May;24(9):5341-5351. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15190. Epub 2020 Mar 31. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32233059 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 and APOA1 mRNA-based therapies for the treatment of experimental acute pancreatitis.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 27;23(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06129-7. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39871339 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 reduces the severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice.Gastroenterology. 2009 Nov;137(5):1795-804. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.064. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19664632
-
Silencing of the Fibroblast growth factor 21 gene is an underlying cause of acinar cell injury in mice lacking MIST1.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Apr 15;306(8):E916-28. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00559.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24549397
-
Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Patients with and without Pterygia.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020 Feb 2;15(1):38-44. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v15i1.5940. eCollection 2020 Jan-Mar. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2020. PMID: 32095207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adipokines and their role in acute pancreatitis.J Med Biochem. 2024 Jun 15;43(4):512-527. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-47515. J Med Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39139157 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of weight loss in patients with obesity treated with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 25;10:1058364. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1058364. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36761216 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against type 2 diabetes in mice by promoting insulin expression and secretion in a PI3K/Akt signaling-dependent manner.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Feb;23(2):1059-1071. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14007. Epub 2018 Nov 20. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30461198 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is robustly induced by ethanol and has a protective role in ethanol associated liver injury.Mol Metab. 2017 Nov;6(11):1395-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.08.004. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29107287 Free PMC article.
-
The Diagnostic Role of FGF 21 in Endometrial Cancer and Other Pathologies of the Uterine Corpus.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 22;13(3):399. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030399. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007;5(6):426–37. Epub 2007/06/07. S1550-4131(07)00129-5 [pii] 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.05.002 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2000;1492(1):203–6. Epub 2000/06/20. S0167-4781(00)00067-1 [pii]. . - PubMed
-
- Dushay J, Chui PC, Gopalakrishnan GS, Varela-Rey M, Crawley M, Fisher FM, et al. Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(2):456–63. Epub 2010/05/11. 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.054 S0016-5085(10)00662-1 [pii]. . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

