Transmission of Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus Produced from Different Recipient Cells In Vivo
- PMID: 27832080
- PMCID: PMC5104465
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165156
Transmission of Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus Produced from Different Recipient Cells In Vivo
Abstract
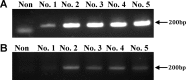
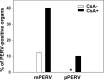
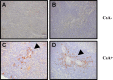
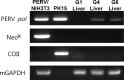
Humanized pigs have been developed to reduce the incidence of immune rejection in xenotransplantation, but significant concerns remain, such as transmission of viral zoonosis. Porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERV), which exist in the genome of pigs, are produced as infectious virions from all porcine cells and cause zoonosis. Here, we examined the possibility of zoonosis of hosts under conditions of immune suppression or xenotransplantation of cells producing host-adapted viruses. Upon transplantation of PERV-producing porcine cells into mice, no transmission of PERV was detected, whereas, transmission of PERV from mice transplanted with mouse-adapted PERV-producing cells was detected. In addition, the frequency of PERV transmission was increased in CsA treated mice transplanted with PERV-producing murine cells, compared with PERV-producing porcine cells. Transmission of PERV to host animals did not affect weight but immune responses, in particular, the number of T cells from PERV-transmitted mice, were notably reduced. The observed risk of PERV zoonosis highlights the requirement for thorough evaluation of viral zoonosis under particular host conditions, such as immunosuppressive treatment and transplantation with host-adapted virus-producing cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The International Xenotransplantation Association consensus statement on conditions for undertaking clinical trials of porcine islet products in type 1 diabetes--chapter 5: Strategies to prevent transmission of porcine endogenous retroviruses.Xenotransplantation. 2009 Jul-Aug;16(4):239-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3089.2009.00544.x. Xenotransplantation. 2009. PMID: 19799764
-
Transient transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus to fetal lambs after pig islet tissue xenotransplantation.Immunol Cell Biol. 2007 Apr-May;85(3):238-48. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100028. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Immunol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17228325
-
In vivo screening of porcine endogenous retrovirus in Chinese Banna minipig inbred.Transplant Proc. 2006 Sep;38(7):2261-3. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2006.06.098. Transplant Proc. 2006. PMID: 16980059
-
Differential sensitivity of porcine endogenous retrovirus to APOBEC3-mediated inhibition.Arch Virol. 2015 Aug;160(8):1901-8. doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2450-y. Epub 2015 May 29. Arch Virol. 2015. PMID: 26016442
-
Can Antiretroviral Drugs Be Used to Treat Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus (PERV) Infection after Xenotransplantation?Viruses. 2017 Aug 8;9(8):213. doi: 10.3390/v9080213. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28786944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reducing porcine corneal graft rejection, with an emphasis on porcine endogenous retrovirus transmission safety: a review.Int J Ophthalmol. 2019 Feb 18;12(2):324-332. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2019.02.21. eCollection 2019. Int J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30809491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of Pig Cells Harboring Porcine Endogenous Retroviruses in Non-Human Primate Bladder After Renal Xenotransplantation.Viruses. 2019 Aug 29;11(9):801. doi: 10.3390/v11090801. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31470671 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of various detergent-based immersion and perfusion decellularization strategies on the novel caprine pancreas derived extracellular matrix scaffold.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 18;11:1253804. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1253804. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37790257 Free PMC article.
-
The MeLiM Minipig: An Original Spontaneous Model to Explore Cutaneous Melanoma Genetic Basis.Front Genet. 2017 Oct 13;8:146. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00146. eCollection 2017. Front Genet. 2017. PMID: 29081790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cooper DK, Keogh AM, Brink J, Corris PA, Klepetko W, Pierson RN, et al. Report of the Xenotransplantation Advisory Committee of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: the present status of xenotransplantation and its potential role in the treatment of end-stage cardiac and pulmonary diseases. The Journal of heart and lung transplantation: the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation. 2000;19(12):1125–65. Epub 2000/12/22. . - PubMed
-
- Gunzburg WH, Salmons B. Xenotransplantation: is the risk of viral infection as great as we thought? Molecular medicine today. 2000;6(5):199–208. Epub 2000/04/27. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

