Cocaine sensitization increases subthreshold activity in dopamine neurons from the ventral tegmental area
- PMID: 27832596
- PMCID: PMC5288483
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00465.2016
Cocaine sensitization increases subthreshold activity in dopamine neurons from the ventral tegmental area
Abstract
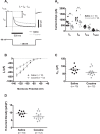
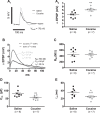
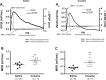
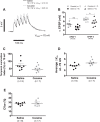
The progressive escalation of psychomotor responses that results from repeated cocaine administration is termed sensitization. This phenomenon alters the intrinsic properties of dopamine (DA) neurons from the ventral tegmental area (VTA), leading to enhanced dopaminergic transmission in the mesocorticolimbic network. The mechanisms underlying this augmented excitation are nonetheless poorly understood. DA neurons display the hyperpolarization-activated, nonselective cation current, dubbed Ih We recently demonstrated that Ih and membrane capacitance are substantially reduced in VTA DA cells from cocaine-sensitized rats. The present study shows that 7 days of cocaine withdrawal did not normalize Ih and capacitance. In cells from cocaine-sensitized animals, the amplitude of excitatory synaptic potentials, at -70 mV, was ∼39% larger in contrast to controls. Raise and decay phases of the synaptic signal were faster under cocaine, a result associated with a reduced membrane time constant. Synaptic summation was paradoxically elevated by cocaine exposure, as it consisted of a significantly reduced summation indexed but a considerably increased depolarization. These effects are at least a consequence of the reduced capacitance. Ih attenuation is unlikely to explain such observations, since at -70 mV, no statistical differences exist in Ih or input resistance. The neuronal shrinkage associated with a diminished capacitance may help to understand two fundamental elements of drug addiction: incentive sensitization and negative emotional states. A reduced cell size may lead to substantial enhancement of cue-triggered bursting, which underlies drug craving and reward anticipation, whereas it could also result in DA depletion, as smaller neurons might express low levels of tyrosine hydroxylase.
New & noteworthy: This work uses a new approach that directly extracts important biophysical parameters from alpha function-evoked synaptic potentials. Two of these parameters are the cell membrane capacitance (Cm) and rate at any time point of the synaptic waveform. The use of such methodology shows that cocaine sensitization reduces Cm and increases the speed of synaptic signaling. Paradoxically, although synaptic potentials show a faster decay under cocaine their temporal summation is substantially elevated.
Keywords: EPSP; capacitance; cocaine; h-current; temporal summation.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Ackerman JM, White FJ. A10 somatodendritic dopamine autoreceptor sensitivity following withdrawal from repeated cocaine treatment. Neurosci Lett 117: 181–187, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Tang XC, Toda S, Kalivas PW. Neuroadaptations in cystine-glutamate exchange underlie cocaine relapse. Nat Neurosci 6: 743–749, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

