Prevalence and socio-economic burden of heart failure in an aging society of South Korea
- PMID: 27832754
- PMCID: PMC5103434
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-016-0404-2
Prevalence and socio-economic burden of heart failure in an aging society of South Korea
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in South Korea. With the rapidly aging population in the country, the prevalence of HF and its associated costs are expected to rise continuously. This study was carried out to estimate the prevalence and economic burden of HF in order to understand its impact on our society.
Methods: A prevalence-based, cost-of-illness study was conducted using the 2014 Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service-National Patients Sample (HIRA-NPS) data. Adult HF patients were defined as those aged ≥19 years who had at least one insurance claim record with a primary or secondary diagnosis of HF (ICD-10 codes of I11.0, I13.0, I13.2, and I50.x). The costs consist of direct costs (i.e., medical and non-medical costs) and indirect costs (i.e., productivity loss cost due to morbidity and premature death). Subgroup analyses were conducted by age group, history of HF hospitalization, and type of universal health security program enrolled in.
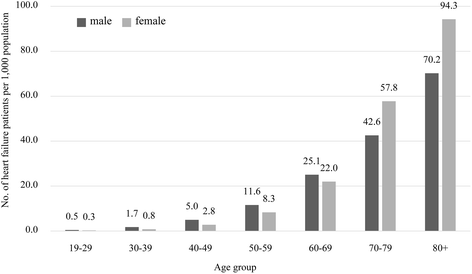
Results: A total of 475,019 adults were identified to have HF in 2014. The estimated prevalence rate of HF was 12.4 persons per 1,000 adults. According to the base cases and the extended definition of the cases, the annual economic burden of HF from a societal perspective ranges from USD 1,414.0 to 1,560.5 for individual patients, and from USD 752.8 million to 1,085.6 million for the country. A high percentage (68.5 %) of this socioeconomic burden consist of medical costs, followed by caregiver's cost (13.2 %), productivity loss costs due to premature death (10.8 %) and morbidity (4.2 %), and transportation costs (3.4 %). The HF patients with prior hospitalization due to HF annually spent 9.7 times more for National-Health-Insurance-covered medical costs compared to HF patients who were not previously hospitalized.
Conclusions: In the present study, HF patients who were older and had a history of prior hospitalization for HF as well as an indigent status were shown at high risk of spending more for healthcare to treat their HF. An effective disease management protocol should be employed to target this patient group.
Keywords: Cost of heart failure; Economic burden; Heart failure; Sensitivity analysis; South Korea.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and socioeconomic burden of diabetes mellitus in South Korean adults: a population-based study using administrative data.BMC Public Health. 2021 Mar 20;21(1):548. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10450-3. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33743612 Free PMC article.
-
The incremental economic burden of heart failure: A population-based investigation from South Korea.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 21;13(12):e0208731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208731. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30576328 Free PMC article.
-
[Socioeconomic costs of stroke in Korea: estimated from the Korea national health insurance claims database].J Prev Med Public Health. 2009 Jul;42(4):251-60. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.2009.42.4.251. J Prev Med Public Health. 2009. PMID: 19675402 Korean.
-
Cost-of-illness studies in heart failure: a systematic review 2004-2016.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 May 2;18(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0815-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29716540 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016 Jun;13(6):368-78. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.25. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26935038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and appropriateness of a scoring method for International Classification of Functioning, Disabilities, and Health assessment in older patients with heart failure: a Delphi survey of expert panel in Japan.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 17;12(9):e060609. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-060609. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36115681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and socioeconomic burden of diabetes mellitus in South Korean adults: a population-based study using administrative data.BMC Public Health. 2021 Mar 20;21(1):548. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10450-3. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33743612 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Heart Failure Management: A Review of the Clinical Pharmacist Integration to the Multidisciplinary Health Care Team.Int J Heart Fail. 2023 Nov 15;6(1):1-10. doi: 10.36628/ijhf.2023.0022. eCollection 2024 Jan. Int J Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 38303921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transitional Care Interventions for Patients with Heart Failure: An Integrative Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 23;17(8):2925. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082925. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32340346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overactive Bladder is a Distress Symptom in Heart Failure.Int Neurourol J. 2018 Jun;22(2):77-82. doi: 10.5213/inj.1836120.060. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Int Neurourol J. 2018. PMID: 29991228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE, Drazner MH, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:e147–239. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.05.019. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous