Spirometric variability in smokers: transitions in COPD diagnosis in a five-year longitudinal study
- PMID: 27832774
- PMCID: PMC5105293
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-016-0468-7
Spirometric variability in smokers: transitions in COPD diagnosis in a five-year longitudinal study
Abstract
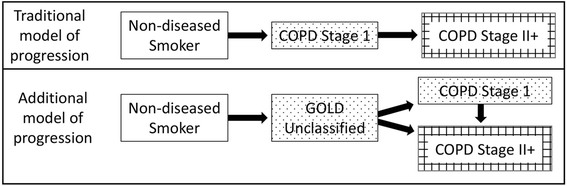
Background: Spirometrically-defined chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is considered progressive but its natural history is inadequately studied. We hypothesized that spirometrically-defined COPD states could undergo beneficial transitions.
Methods: Participants in the Lovelace Smokers' Cohort (n = 1553), primarily women, were longitudinally studied over 5 years. Spirometric states included normal postbronchodilator spirometry, COPD Stage I, Unclassified state, and COPD Stage II+, as defined by GOLD guidelines. Beneficial transitions included either a decrease in disease severity, including resolution of spirometric abnormality, or maintenance of non-diseased state. 'All smokers' (n = 1553) and subgroups with normal and abnormal spirometry at baseline (n = 956 and 597 respectively) were separately analyzed. Markov-like model of transition probabilities over an average follow-up period of 5 years were calculated.
Results: Among 'all smokers', COPD Stage I, Unclassified, and COPD Stage II+ states were associated with probabilities of 16, 39, and 22 % respectively for beneficial transitions, and of 16, 35, and 4 % respectively for resolution. Beneficial transitions were more common for new-onset disease than for pre-existing disease (p < 0.001). Beneficial transitions were less common among older smokers, men, or those with bronchial hyperresponsiveness but more common among Hispanics and smokers with excess weight.
Conclusions: This observational study of ever smokers, shows that spirometrically-defined COPD states, may not be uniformly progressive and can improve or resolve over time. The implication of these findings is that the spirometric diagnosis of COPD can be unstable. Furthermore, COPD may have a pre-disease state when interventions might help reverse or change its natural history.
Trial registration: NA.
Figures

References
-
- Trends in COPD (Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema): Morbidity and Mortality (http://www.lungusa.org/finding-cures/our-research/trend-reports/copd-tre...). Accessed 7 Jan 2016.
-
- World Health Organization Media Center: The top 10 causes of death: The 10 leading causes of death in the world, 2000 and 2012, available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/. Accessed 7 Jan 2016. In Fact sheet number 310; May 2014.
-
- Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1256–1276. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.5.2101039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aalen OO, Farewell VT, De Angelis D, Day NE, Gill ON. A Markov model for HIV disease progression including the effect of HIV diagnosis and treatment: application to AIDS prediction in England and Wales. Stat Med. 1997;16:2191–2210. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19971015)16:19<2191::AID-SIM645>3.0.CO;2-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

