miR-199a-3p inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting YAP1, suppressing Jagged1-Notch signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27832779
- PMCID: PMC5103406
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-016-0295-7
miR-199a-3p inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting YAP1, suppressing Jagged1-Notch signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
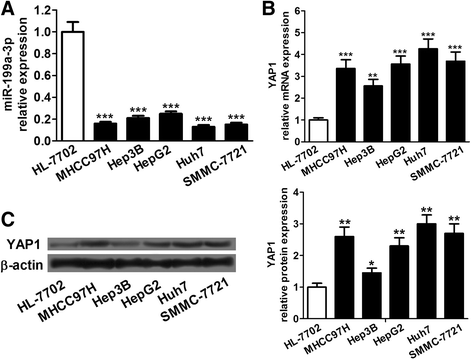
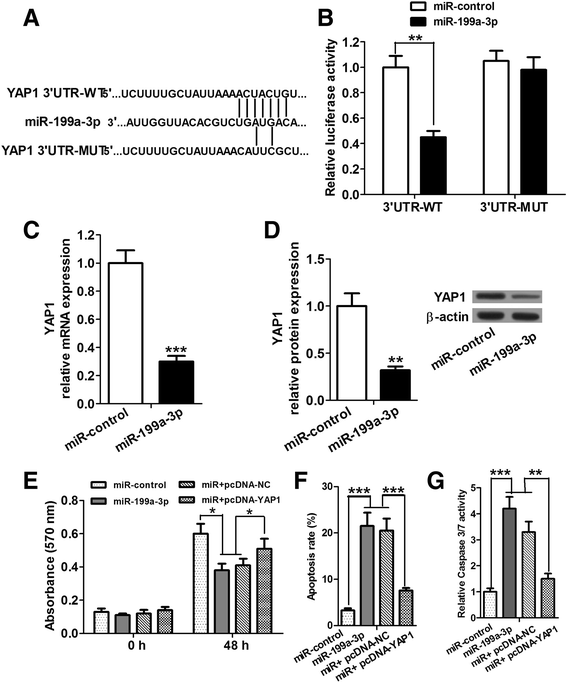
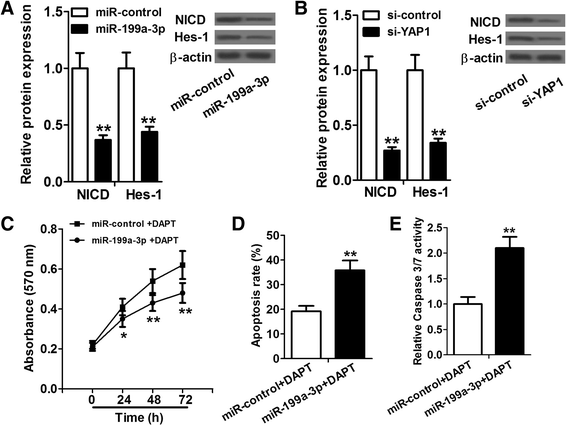
Background: miR-199a-3p was significantly downregulated in the majority of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and HCC cell lines. Yes associated protein 1 (YAP1) was overexpressed in human HCC, which promoted HCC development and progression by upregulating Jagged1 and activating the Notch pathway. We searched potential targets of miR-199a-3p with DIANA, TargetScan and PicTar tools, and found that YAP1 is one of the potential targets. Based on these findings, we speculated that miR-199a-3p might suppress HCC growth by targeting YAP1, downregulating Jagged1 and suppressing the Notch pathway.
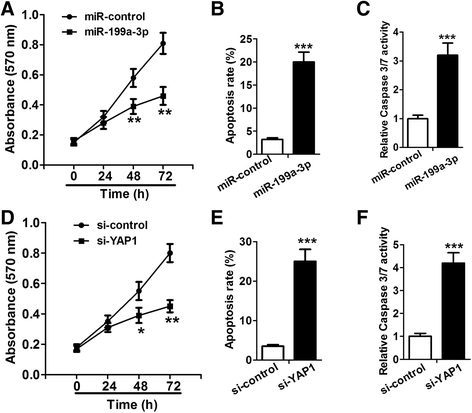
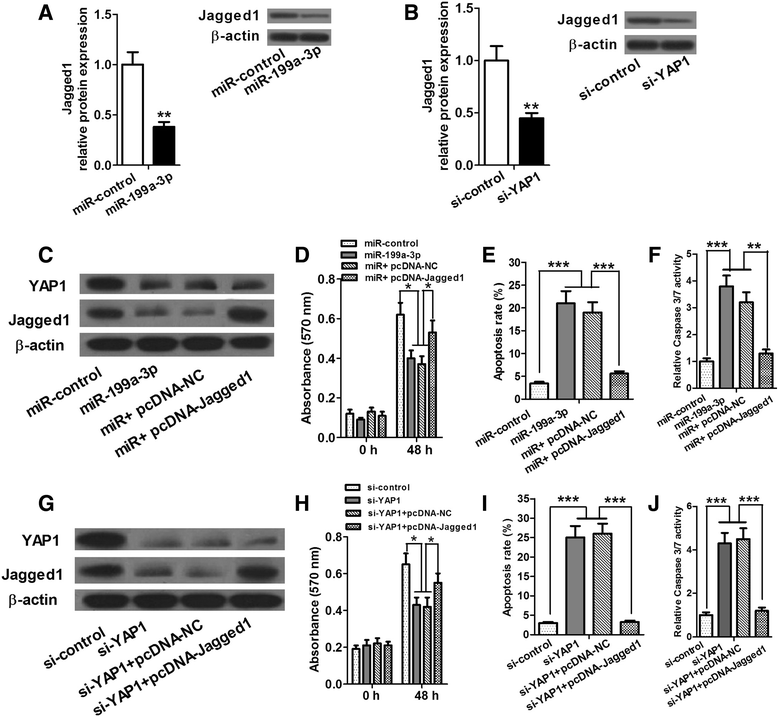
Results: We determined the expression of miR-199a-3p and YAP1 by quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blot assays, respectively, and found downregulation of miR-199a-3p and upregulation of YAP1 in HCC cell lines. Cell proliferation and apoptosis assays showed that miR-199a-3p suppresses HCC cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis, and knockdown of YAP1 has similar role. Furthermore, we verified that miR-199a-3p can directly target YAP1. We further investigated and confirmed that miR-199a-3p and YAP1 regulate HCC cell proliferation and apoptosis through Jagged1-Notch signaling.
Conclusion: miR-199a-3p targets YAP1, downregulates Jagged1 and suppresses the Notch signaling to inhibit HCC cell proliferation and promote apoptosis. These findings provide new insights into the mechanism by which miR-199a-3p suppresses HCC cell proliferation and induces apoptosis.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Jagged1; Notch signaling; Yes associated protein 1; miR-199a-3p.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circ-ZEB1 promotes PIK3CA expression by silencing miR-199a-3p and affects the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 11;21(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01529-5. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35277182 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-222-3p induced by hepatitis B virus promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by upregulating THBS1.Hum Cell. 2021 Nov;34(6):1788-1799. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00577-1. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34273068
-
Anti-invasion and anti-migration effects of miR-199a-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma are due in part to targeting CD151.Int J Oncol. 2016 Nov;49(5):2037-2045. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3677. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27599545
-
Targeting the Hippo/YAP1 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: From mechanisms to therapeutic drugs (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Sep;65(3):88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5676. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39092548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current research of the Notch pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Med Res. 2025 May 20;30(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02626-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40394648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated analysis using ToppMiR uncovers altered miRNA- mRNA regulatory networks in pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma-A pilot study.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Jan;6(1):e1685. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1685. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 35859536 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of miRNAs in Dexmedetomidine's Neuroprotective Effects against Brain Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 13;23(10):5452. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105452. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC00346 Acts as a Competing Endogenous RNA Regulating Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Modulating CDK1/CCNB1 Axis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 18;8:54. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00054. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32133348 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Extracellular Vesicles in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Emergent Perspectives.Cells. 2023 Jul 1;12(13):1763. doi: 10.3390/cells12131763. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and their role in environmental chemical carcinogenesis.Environ Geochem Health. 2019 Feb;41(1):225-247. doi: 10.1007/s10653-018-0179-8. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Environ Geochem Health. 2019. PMID: 30171477 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

