New Concepts in Dopamine D2 Receptor Biased Signaling and Implications for Schizophrenia Therapy
- PMID: 27832841
- PMCID: PMC5702557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.10.011
New Concepts in Dopamine D2 Receptor Biased Signaling and Implications for Schizophrenia Therapy
Abstract
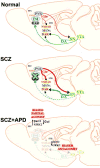
The dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) is a G protein-coupled receptor that is a common target for antipsychotic drugs. Antagonism of D2R signaling in the striatum is thought to be the primary mode of action of antipsychotic drugs in alleviating psychotic symptoms. However, antipsychotic drugs are not clinically effective at reversing cortical-related symptoms, such as cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. While the exact mechanistic underpinnings of these cognitive deficits are largely unknown, deficits in cortical dopamine function likely play a contributing role. It is now recognized that similar to most G protein-coupled receptors, D2Rs signal not only through canonical G protein pathways but also through noncanonical beta-arrestin2-dependent pathways. We review the current mechanistic bases for this dual signaling mode of D2Rs and how these new concepts might be leveraged for therapeutic gain to target both cortical and striatal dysfunction in dopamine neurotransmission and hence have the potential to correct both positive and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Keywords: Antipsychotics; Arrestin; Dopamine; Functional selectivity; Schizophrenia; System bias.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
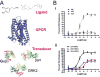
 ), enhanced activity (
), enhanced activity (
 ) and reduced activity (
) and reduced activity (
 ).
).References
-
- Kebabian JW, Calne DB. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979;277:93–96. - PubMed
-
- Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG. Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiological reviews. 1998;78:189–225. - PubMed
-
- Benovic JL, Strasser RH, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1986;83:2797–2801. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lohse MJ, Benovic JL, Codina J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. beta-Arrestin: a protein that regulates beta-adrenergic receptor function. Science (New York, NY. 1990;248:1547–1550. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson SS, Downey WE, 3rd, Colapietro AM, Barak LS, Menard L, Caron MG. Role of beta-arrestin in mediating agonist-promoted G protein-coupled receptor internalization. Science (New York, NY. 1996;271:363–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

