IGF-1/IGF-1R/hsa-let-7c axis regulates the committed differentiation of stem cells from apical papilla
- PMID: 27833148
- PMCID: PMC5105129
- DOI: 10.1038/srep36922
IGF-1/IGF-1R/hsa-let-7c axis regulates the committed differentiation of stem cells from apical papilla
Abstract
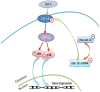
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and its receptor IGF-1R play a paramount role in tooth/bone formation while hsa-let-7c actively participates in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. However, the interaction between IGF-1/IGF-1R and hsa-let-7c on the committed differentiation of stem cells from apical papilla (SCAPs) remains unclear. In this study, human SCAPs were isolated and treated with IGF-1 and hsa-let-7c over/low-expression viruses. The odonto/osteogenic differentiation of these stem cells and the involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway were subsequently investigated. Alizarin red staining showed that hsa-let-7c low-expression can significantly promote the mineralization of IGF-1 treated SCAPs, while hsa-let-7c over-expression can decrease the calcium deposition of IGF-1 treated SCAPs. Western blot assay and real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction further demonstrated that the expression of odonto/osteogenic markers (ALP, RUNX2/RUNX2, OSX/OSX, OCN/OCN, COL-I/COL-I, DSPP/DSP, and DMP-1/DMP-1) in IGF-1 treated SCAPs were significantly upregulated in Let-7c-low group. On the contrary, hsa-let-7c over-expression could downregulate the expression of these odonto/osteogenic markers. Moreover, western blot assay showed that the JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways were activated in Let-7c-low SCAPs but inhibited in Let-7c-over SCAPs. Together, the IGF-1/IGF-1R/hsa-let-7c axis can control the odonto/osteogenic differentiation of IGF-1-treated SCAPs via the regulation of JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Yunnan Baiyao Conditioned Medium Promotes the Odonto/Osteogenic Capacity of Stem Cells from Apical Papilla via Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 23;2019:9327386. doi: 10.1155/2019/9327386. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31179335 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA hsa-let-7b suppresses the odonto/osteogenic differentiation capacity of stem cells from apical papilla by targeting MMP1.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Aug;119(8):6545-6554. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26737. Epub 2018 May 8. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29384216
-
Hsa-let-7c controls the committed differentiation of IGF-1-treated mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulps by targeting IGF-1R via the MAPK pathways.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Apr 13;50(4):1-14. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0048-7. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29650947 Free PMC article.
-
Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla: A Promising Source for Stem Cell-Based Therapy.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jan 29;2019:6104738. doi: 10.1155/2019/6104738. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30834270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the insulin‑like growth factor (IGF) axis in osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Apr;71(8):1469-76. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1508-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24232361 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noncoding RNAs: new insights into the odontogenic differentiation of dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Sep 23;10(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1411-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31547871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The odontoblastic differentiation of dental mesenchymal stem cells: molecular regulation mechanism and related genetic syndromes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 25;11:1174579. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1174579. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37818127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blue light-emitting diode promotes mineralization of stem cells from the apical papilla via cryptochrome 1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling.J Mol Histol. 2025 Apr 1;56(2):125. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10400-y. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40167571
-
Yunnan Baiyao Conditioned Medium Promotes the Odonto/Osteogenic Capacity of Stem Cells from Apical Papilla via Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 23;2019:9327386. doi: 10.1155/2019/9327386. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31179335 Free PMC article.
-
Superior protective effects of PGE2 priming mesenchymal stem cells against LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) through macrophage immunomodulation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Mar 22;14(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03277-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36949464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Estrela C., Alencar A. H., Kitten G. T., Vencio E. F. & Gava E. Mesenchymal stem cells in the dental tissues: perspectives for tissue regeneration. Braz Dent J 22, 91–98 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Standards for the assessment of estrogen receptors in human breast cancer. Report of a workshop on September 29, 1972, at the Antoni van Leeuwenhoek-Huis, Amsterdam. Eur J Cancer 9, 379–381 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Liu D. et al.. Demethylation of IGFBP5 by Histone Demethylase KDM6B Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Periodontal Tissue Regeneration by Enhancing Osteogenic Differentiation and Anti-Inflammation Potentials. Stem Cells 33, 2523–2536 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

