Interaction of the Nitrogen Regulatory Protein GlnB (PII) with Biotin Carboxyl Carrier Protein (BCCP) Controls Acetyl-CoA Levels in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
- PMID: 27833596
- PMCID: PMC5080355
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01700
Interaction of the Nitrogen Regulatory Protein GlnB (PII) with Biotin Carboxyl Carrier Protein (BCCP) Controls Acetyl-CoA Levels in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Abstract
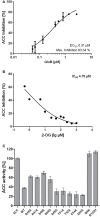
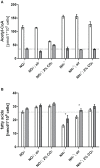
The family of PII signal transduction proteins (members GlnB, GlnK, NifI) plays key roles in various cellular processes related to nitrogen metabolism at different functional levels. Recent studies implied that PII proteins may also be involved in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism, since GlnB proteins from Proteobacteria and from Arabidopsis thaliana were shown to interact with biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC). In case of Escherichia coli ACCase, this interaction reduces the kcat of acetyl-CoA carboxylation, which should have a marked impact on the acetyl-CoA metabolism. In this study we show that the PII protein of a unicellular cyanobacterium inhibits the biosynthetic activity of E. coli ACC and also interacts with cyanobacterial BCCP in an ATP and 2-oxoglutarate dependent manner. In a PII mutant strain of Synechocystis strain PCC 6803, the lacking control leads to reduced acetyl-CoA levels, slightly increased levels of fatty acids and formation of lipid bodies as well as an altered fatty acid composition.
Keywords: BCCP; GlnB (PII); Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803; acetyl-CoA; cyanobacteria.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

