EPIDEMIOLOGY, PATHOGENESIS and DIAGNOSIS of LYMPHANGIOLEIOMYOMATOSIS
- PMID: 27833825
- PMCID: PMC5098502
- DOI: 10.1517/21678707.2016.1148597
EPIDEMIOLOGY, PATHOGENESIS and DIAGNOSIS of LYMPHANGIOLEIOMYOMATOSIS
Abstract
Introduction: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a disease of women characterized by cystic lung destruction, lymphatic involvement, and renal angiomyolipomas.
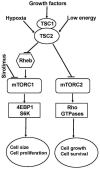
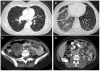
Areas covered: LAM is caused by proliferation of abnormal smooth muscle-like LAM cells containing mutations and perhaps epigenetic modifications of the TSC1 or TSC2 genes, which encode, respectively, hamartin and tuberin, two proteins controlling the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. LAM occurs sporadically or in association with tuberous sclerosis complex. LAM may present with dyspnea, recurrent pneumothorax or chylothorax. Pulmonary function tests show reduced flow rates and lung diffusion capacity. Exercise testing may reveal hypoxemia and ventilatory limitation. The severity and progression of disease may be assessed by computer tomography, and pulmonary function and exercise testing. mTOR inhibitors, (e.g., sirolimus) are effective in stabilizing lung function, and reducing the size of chylous effusions, lymphangioleiomyomas, and angiomyolipomas.
Expert opinion: Different clinical phenotypes including variable rates of disease progression and variable responses to therapy are seen in LAM patients. No one test is available that predicts the course of disease at the time of diagnosis. Further research regarding the molecular biology of LAM clinical phenotypes is warranted. Recent advances in the characterization of the pathogenesis of LAM are leading to the development of new therapies.
Keywords: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis; TSC 1 and TSC2 mutations; Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC); mTOR.
Figures


References
-
-
Ryu JH, Moss J, Beck GJ, et al. The NHLBI Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Registry. Characteristics of 230 Patients at Enrollment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:105–11. This article reports the results from the LAM Registry study.
-
-
- McCormack FX. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a clinical update. Chest. 2008;133:507–16. - PubMed
-
- Ferrans VJ, Yu ZX, Nelson WK, et al. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM). A review of clinical and morphological features. J Nippon Med Sch. 2000;67:311–29. - PubMed
-
-
Matsui K, Tatsuguchi A, Valencia J, et al. Extrapulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): Clinicopathologic features in 22 cases. Hum Pathol. 2000;31:1242–48. References and 4 contain good descriptions of the histopathology of LAM.
-
-
- Harknett EC, Chang WY, Byrnes S, et al. Use of variability in national and regional data to estimate the prevalence of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Q J Med. 2011;104:971–19. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
