Development and Evaluation of a Duplex Real-Time PCR Assay With a Novel Internal Standard for Precise Quantification of Plasma DNA
- PMID: 27834061
- PMCID: PMC5107613
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.18
Development and Evaluation of a Duplex Real-Time PCR Assay With a Novel Internal Standard for Precise Quantification of Plasma DNA
Abstract
Background: Circulating levels of cell-free DNA increase in many pathologic conditions. However, notable discrepancies in the quantitative analysis of cell-free DNA from a large number of laboratories have become a considerable pitfall, hampering its clinical application.
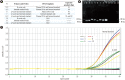
Methods: We designed a novel recombinant DNA fragment that could be applied as an internal standard in a newly developed and validated duplex real-time PCR assay for the quantitative analysis of total cell-free plasma DNA, which was tested in 5,442 healthy adults and 200 trauma patients.
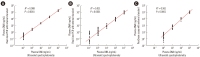
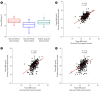
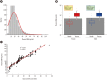
Results: Compared with two traditional methods, this novel assay showed a lower detection limit of 0.1 ng/mL, lower intra- and inter-assay CVs, and higher accuracy in the recovery test. The median plasma DNA concentration of healthy males (20.3 ng/mL, n=3,092) was significantly higher than that of healthy females (16.1 ng/mL, n=2,350) (Mann-Whitney two-sample rank sum test, P<0.0001). The reference intervals of plasma DNA concentration were 0-45.8 ng/mL and 0-52.5 ng/mL for healthy females and males, respectively. The plasma DNA concentrations of the majority of trauma patients (96%) were higher than the upper normal cutoff values and were closely related to the corresponding injury severity scores (R²=0.916, P<0.0001).
Conclusions: This duplex real-time PCR assay with a new internal standard could eliminate variation and allow for more sensitive, repeatable, accurate, and stable quantitative measurements of plasma DNA, showing promising application in clinical diagnosis.
Keywords: Duplex PCR; Internal standard; Plasma DNA; Quantification; Reference interval; Trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest: No potential conflicts of interests relevant to this article were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Mandel P, Metais P. Nucleic acids in plasma samples from human blood. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1948;142:241–243. - PubMed
-
- Leon SA, Shapiro B, Sklaroff DM, Yaros MJ. Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy. Cancer Res. 1977;37:646–650. - PubMed
-
- Tong YK, Lo YM. Diagnostic developments involving cell-free (circulating) nucleic acids. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;363:187–196. - PubMed
-
- Tissot C, Toffart AC, Villar S, Souquet PJ, Merle P, Moro-Sibilot D, et al. Circulating free DNA concentration is an independent prognostic biomarker in lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 2015;46:1773–1780. - PubMed
-
- Sozzi G, Roz L, Conte D, Mariani L, Andriani F, Lo Vullo S, et al. Plasma DNA quantification in lung cancer computed tomography screening: five-year results of a prospective study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:69–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

