Evaluation of BD MAX Staph SR Assay for Differentiating Between Staphylococcus aureus and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Determining Methicillin Resistance Directly From Positive Blood Cultures
- PMID: 27834064
- PMCID: PMC5107616
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.39
Evaluation of BD MAX Staph SR Assay for Differentiating Between Staphylococcus aureus and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Determining Methicillin Resistance Directly From Positive Blood Cultures
Abstract
Background: We evaluated the performance of the BD MAX StaphSR Assay (SR assay; BD, USA) for direct detection of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistance not only in S. aureus but also in coagulase-negative Staphylococci (CNS) from positive blood cultures.
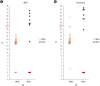
Methods: From 228 blood culture bottles, 103 S. aureus [45 methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), 55 methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA), 3 mixed infections (1 MRSA+Enterococcus faecalis, 1 MSSA+MRCNS, 1 MSSA+MSCNS)], and 125 CNS (102 MRCNS, 23 MSCNS) were identified by Vitek 2. For further analysis, we obtained the cycle threshold (Ct) values from the BD MAX system software to determine an appropriate cutoff value. For discrepancy analysis, conventional mecA/mecC PCR and oxacillin minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined.
Results: Compared to Vitek 2, the SR assay identified all 103 S. aureus isolates correctly but failed to detect methicillin resistance in three MRSA isolates. All 55 MSSA isolates were correctly identified by the SR assay. In the concordant cases, the highest Ct values for nuc, mecA, and mec right-extremity junction (MREJ) were 25.6, 22, and 22.2, respectively. Therefore, we selected Ct values from 0-27 as a range of positivity, and applying this cutoff, the sensitivity/specificity of the SR assay were 100%/100% for detecting S. aureus, and 97.9%/98.1% and 99.0%/95.8% for detecting methicillin resistance in S. aureus and CNS, respectively.
Conclusions: We propose a Ct cutoff value for nuc/mec assay without considering MREJ because mixed cultures of MSSA and MRCNS were very rare (0.4%) in the positive blood cultures.
Keywords: BD MAX; Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus; Ct value; MREJ; MRSA; Methicillin; Staph SR.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Snyder JW, Munier GK, Heckman SA, Camp P, Overman TL. Failure of the BD GeneOhm StaphSR assay for direct detection of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates in positive blood cultures collected in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47:3747–3748. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Savithri MB, Iyer V, Jones M, Yarwood T, Looke D, Kruger PS, et al. Epidemiology and significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated in blood cultures from critically ill adult patients. Crit Care Resusc. 2011;13:103–107. - PubMed
-
- Rogers KL, Fey PD, Rupp ME. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2009;23:73–98. - PubMed
-
- Pasanen T, Korkeila M, Mero S, Tarkka E, Piiparinen H, Vnopio-Varkila J, et al. A selective broth enrichment combined with real-time nuc-mecA-PCR in the exclusion of MRSA. Apmis. 2010;118:74–80. - PubMed
-
- BD Diagnostics Sparks. MD, USA: 2013. BD MAX StaphSR [package insert]. Catalog no. 442999, publication P0153 (01)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

