Early Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Cognitive Markers of Hereditary Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
- PMID: 27834748
- PMCID: PMC5127744
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.014418
Early Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Cognitive Markers of Hereditary Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
Abstract
Background and purpose: Early markers for cerebral amyloid angiopathy are largely unknown. We aimed to identify which magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (performed at 7 and 3T) and cognitive markers are an early sign in (pre) symptomatic subjects with hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis-Dutch type.
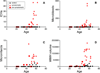
Methods: Twenty-seven DNA-proven Dutch-type mutation carriers (15 symptomatic and 12 presymptomatic) (mean age of 45.9 years) and 33 controls (mean age of 45.6 years) were included. 7T and 3T MRI was performed, cerebral amyloid angiopathy and small-vessel disease type MRI markers were estimated, and cognitive performance was assessed. Univariate general linear modeling analysis was used to assess the association between MRI markers and cognitive performance on the one hand and on the other, mutation status, adjusted for age, sex, and education.
Results: In symptomatic patients, all established cerebral amyloid angiopathy MRI markers (microbleeds, intracerebral hemorrhages, subarachnoid hemorrhages, superficial siderosis, microinfarcts, volume of white matter hyperintensities, and dilated perivascular spaces in centrum semiovale) were increased compared with controls (P<0.05). In presymptomatic subjects, the prevalence of microinfarcts and median volume of white matter hyperintensities were increased in comparison to controls (P<0.05). Symptomatic patients performed worse on all cognitive domains, whereas presymptomatic subjects did not show differences in comparison with controls (P<0.05).
Conclusions: White matter hyperintensities and microinfarcts are more prevalent among presymptomatic subjects and precede cognitive and neuropsychiatric symptoms and intracerebral hemorrhages.
Keywords: cerebral amyloid angiopathy; cognition; hemorrhage; magnetic resonance imaging; siderosis.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bornebroek M, van Buchem MA, Haan J, Brand R, Lanser JB, de Bruine FT, et al. Hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis-dutch type: Better correlation of cognitive deterioration with advancing age than with number of focal lesions or white matter hyperintensities. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1996;10:224–231. - PubMed
-
- Haan J, Algra PR, Roos RA. Hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis-dutch type. Clinical and computed tomographic analysis of 24 cases. Arch. Neurol. 1990;47:649–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical