Selective function-blocking monoclonal human antibody highlights the important role of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) in metastasis
- PMID: 27835863
- PMCID: PMC5356841
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13157
Selective function-blocking monoclonal human antibody highlights the important role of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) in metastasis
Abstract
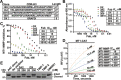
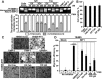
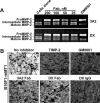
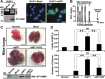
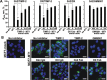
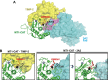
The invasion-promoting MT1-MMP is a cell surface-associated collagenase with a plethora of critical cellular functions. There is a consensus that MT1-MMP is a key protease in aberrant pericellular proteolysis in migrating cancer cells and, accordingly, a promising drug target. Because of high homology in the MMP family and a limited success in the design of selective small-molecule inhibitors, it became evident that the inhibitor specificity is required for selective and successful MT1-MMP therapies. Using the human Fab antibody library (over 1.25×109 individual variants) that exhibited the extended, 23-27 residue long, VH CDR-H3 segments, we isolated a panel of the inhibitory antibody fragments, from which the 3A2 Fab outperformed others as a specific and potent, low nanomolar range, inhibitor of MT1-MMP. Here, we report the in-depth characterization of the 3A2 antibody. Our multiple in vitro and cell-based tests and assays, and extensive structural modeling of the antibody/protease interactions suggest that the antibody epitope involves the residues proximal to the protease catalytic site and that, in contrast with tissue inhibitor-2 of MMPs (TIMP-2), the 3A2 Fab inactivates the protease functionality by binding to the catalytic domain outside the active site cavity. In agreement with the studies in metastasis by others, our animal studies in acute pulmonary melanoma metastasis support a key role of MT1-MMP in metastatic process. Conversely, the selective anti-MT1-MMP monotherapy significantly alleviated melanoma metastatic burden. It is likely that further affinity maturation of the 3A2 Fab will result in the lead inhibitor and a proof-of-concept for MT1-MMP targeting in metastatic cancers.
Keywords: MT1-MMP; antibody; cancer; metastasis; proteinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition mechanism of membrane metalloprotease by an exosite-swiveling conformational antibody.Structure. 2015 Jan 6;23(1):104-115. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Structure. 2015. PMID: 25482542
-
Active-site MMP-selective antibody inhibitors discovered from convex paratope synthetic libraries.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 27;113(52):14970-14975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1609375114. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27965386 Free PMC article.
-
The thiirane-based selective MT1-MMP/MMP2 inhibitor ND-322 reduces melanoma tumor growth and delays metastatic dissemination.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Nov;113(Pt A):515-520. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.033. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27687955 Free PMC article.
-
The membrane tethered matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP at the forefront of melanoma cell invasion and metastasis.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 May 21. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27221755 Review.
-
Coordinate action of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) and MMP-2 enhances pericellular proteolysis and invasion.Cancer Sci. 2010 Apr;101(4):843-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01498.x. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20148894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control of SARS-CoV-2 infection by MT1-MMP-mediated shedding of ACE2.Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 23;13(1):7907. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35590-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36564389 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into natural product inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases.Medchemcomm. 2019 Oct 7;10(12):2024-2037. doi: 10.1039/c9md00165d. eCollection 2019 Dec 1. Medchemcomm. 2019. PMID: 32904148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of a novel camelid-inspired human antibody demonstrates the importance of MMP-14 to cancer stem cell function in the metastatic process.Oncotarget. 2018 Jun 29;9(50):29431-29444. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25654. eCollection 2018 Jun 29. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30034628 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Antibodies Designed for Matrix Metalloproteinase Modulation.Molecules. 2019 Jun 18;24(12):2265. doi: 10.3390/molecules24122265. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31216704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal antibodies against metzincin targets.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;176(1):52-66. doi: 10.1111/bph.14186. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29488211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gingras D, Beliveau R. Emerging concepts in the regulation of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1803:142–150. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalo P, Moreno V, Galvez BG, Arroyo AG. MT1-MMP and integrins: Hand-to-hand in cell communication. Biofactors. 2010;36:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Wolf K, Friedl P. Mapping proteolytic cancer cell-extracellular matrix interfaces. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26:289–298. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

