Tuftsin prevents the negative immunoregulation of neuropilin-1highCD4+CD25+Regulatory T cells and improves survival rate in septic mice
- PMID: 27835904
- PMCID: PMC5348430
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13235
Tuftsin prevents the negative immunoregulation of neuropilin-1highCD4+CD25+Regulatory T cells and improves survival rate in septic mice
Abstract
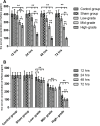
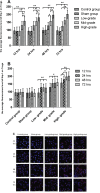
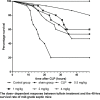
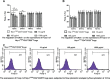
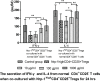
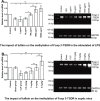
Our previous research showed that neuropilin (Nrp) -1highCD4+CD25+Regulatory T cells (Tregs) exhibited primary negative immunoregulation in sepsis induced immune dysfunction. Tuftsin is the typical ligand of Nrp-1. Herein, we investigated the potential therapeutic value and mechanisms of tuftsin in sepsis. Sepsis per se markedly decreased the serum concentration of tuftsin, administration of tuftsin improved the survival rate of septic mice with cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). In vitro study, tuftsin prevented the negative immunoregulation of Nrp-1highCD4+CD25+Tregs, including weakening the expression of forkhead/winged helix transcription factor (Foxp)- 3/cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen (CTLA)-4, inhibiting the secretion of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and weakening the immunosuppressive function of Nrp-1highCD4+CD25+Tregs to conventional CD4+CD25-T cells. Tuftsin markedly inhibited the demethylation of Foxp3-Tregs specific demethylated region (TSDR) of Nrp-1highCD4+CD25+Tregs. Tuftsin could represent a new potential therapeutic agentia to improve the outcome of septic mice, and associate with preventing the negative immunoregulation of Tregs via Nrp-1.
Keywords: negative immunoregulation; neuropilin-1; regulatory T cells; sepsis; tuftsin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
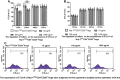
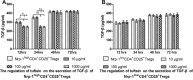
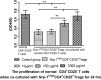
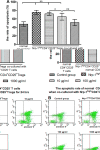
Similar articles
-
Neuropilin-1highCD4⁺CD25⁺ Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Primary Negative Immunoregulation in Sepsis.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:7132158. doi: 10.1155/2016/7132158. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. Retraction in: Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Sep 18;2020:9195623. doi: 10.1155/2020/9195623. PMID: 27239104 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Tuftsin-derived T-peptide prevents cellular immunosuppression and improves survival rate in septic mice.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 18;5:16725. doi: 10.1038/srep16725. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26577833 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Neuropilin-1 Suppresses the Stability of CD4+ CD25+ Regulatory T Cells via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Sepsis.Infect Immun. 2021 Jan 19;89(2):e00399-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00399-20. Print 2021 Jan 19. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 33139385 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and TGF-beta-induced Foxp3(+)CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells are not mirror images of each other.Trends Immunol. 2008 Sep;29(9):429-35. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.06.005. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Trends Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18676178 Review.
-
The emerging role of anti-CD25 directed therapies as both immune modulators and targeted agents in cancer.Br J Haematol. 2017 Oct;179(1):20-35. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14770. Epub 2017 May 30. Br J Haematol. 2017. PMID: 28556984 Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: The Parenteral Vitamin C Improves Sepsis and Sepsis-Induced Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome via Preventing Cellular Immunosuppression.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Sep 4;2020:8462563. doi: 10.1155/2020/8462563. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32952443 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Histone H3 Induces Pyroptosis During Sepsis and May Act Through NOD2 and VSIG4/NLRP3 Pathways.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 5;10:196. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00196. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32432055 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Neuropilin-1highCD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Primary Negative Immunoregulation in Sepsis.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Sep 18;2020:9195623. doi: 10.1155/2020/9195623. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 33013199 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Thymoquinone in Cardiac Damage Caused by Sepsis from BALB/c Mice.Inflammation. 2019 Apr;42(2):516-525. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0909-1. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30343389
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2626c-derived peptide as a therapeutic agent for sepsis.EMBO Mol Med. 2020 Dec 7;12(12):e12497. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202012497. Epub 2020 Dec 1. EMBO Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33258196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Pilcher D, Cooper DJ, Bellomo R. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria in defining severe sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1629–1638. - PubMed
-
- Gaieski DF, Edwards JM, Kallan MJ, Carr BG. Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:1167–1174. - PubMed
-
- Winters BD, Eberlein M, Leung J, Needham DM, Pronovost PJ, Sevransky JE. Long-term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:1276–1283. - PubMed
-
- Huo R, Wang L, Wang X, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zhao X, Chang L, Liu SL, Tong D, Zhang H, Huang Y. Removal of regulatory T cells prevents secondary chronic infection but increases the mortality of subsequent sub-acute infection in sepsis mice. Oncotarget. 2016;7:10962–10975. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7682. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

