In vitro to in vivo extrapolation of the complex drug-drug interaction of bupropion and its metabolites with CYP2D6; simultaneous reversible inhibition and CYP2D6 downregulation
- PMID: 27836670
- PMCID: PMC5164944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.11.007
In vitro to in vivo extrapolation of the complex drug-drug interaction of bupropion and its metabolites with CYP2D6; simultaneous reversible inhibition and CYP2D6 downregulation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "In vitro to in vivo extrapolation of the complex drug-drug interaction of bupropion and its metabolites with CYP2D6; simultaneous reversible inhibition and CYP2D6 downregulation" [Biochem. Pharmacol. 123(2017)85-96].Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;183:114306. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114306. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33161206 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
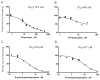
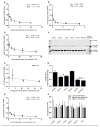
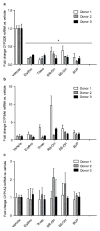
Bupropion is a widely used antidepressant and smoking cessation aid and a strong inhibitor of CYP2D6 in vivo. Bupropion is administered as a racemic mixture of R- and S-bupropion and has stereoselective pharmacokinetics. Four primary metabolites of bupropion, threo- and erythro-hydrobupropion and R,R- and S,S-OH-bupropion, circulate at higher concentrations than the parent drug and are believed to contribute to the efficacy and side effects of bupropion as well as to the CYP2D6 inhibition. However, bupropion and its metabolites are only weak inhibitors of CYP2D6 in vitro, and the magnitude of the in vivo drug-drug interactions (DDI) caused by bupropion cannot be explained by the in vitro data even when CYP2D6 inhibition by the metabolites is accounted for. The aim of this study was to quantitatively explain the in vivo CYP2D6 DDI magnitude by in vitro DDI data. Bupropion and its metabolites were found to inhibit CYP2D6 stereoselectively with up to 10-fold difference in inhibition potency between enantiomers. However, the reversible inhibition or active uptake into hepatocytes did not explain the in vivo DDIs. In HepG2 cells and in plated human hepatocytes bupropion and its metabolites were found to significantly downregulate CYP2D6 mRNA in a concentration dependent manner. The in vivo DDI was quantitatively predicted by significant down-regulation of CYP2D6 mRNA and reversible inhibition of CYP2D6 by bupropion and its metabolites. This study is the first example of a clinical DDI resulting from CYP down-regulation and first demonstration of a CYP2D6 interaction resulting from transcriptional regulation.
Keywords: Bupropion; CYP2D6; Drug-drug interactions; Enzyme regulation; In vitro to in vivo extrapolation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest with the current work.
Figures
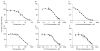
References
-
- Bohnert T, Patel A, Templeton I, Chen Y, Lu C, Lai G, Leung L, Tse S, Einolf HJ, Wang YH, Sinz M, Stearns R, Walsky R, Geng W, Sudsakorn S, He L, Wahlstrom J, Keirns J, Narayanan R, Lang D, Yang X. Evaluation of a New Molecular Entity as a Victim of Metabolic Drug-Drug Interactions - an Industry Perspective. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.069096. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vieira MLT, Kirby B, Ragueneau-Majlessi I, Galetin A, Chien JYL, Einolf HJ, Fahmi OA, Fischer V, Fretland A, Grime K, Hall SD, Higgs R, Plowchalk D, Riley R, Seibert E, Skordos K, Snoeys J, Venkatakrishnan K, Waterhouse T, Obach RS, Berglund EG, Zhang L, Zhao P, Reynolds KS, Huang S-M. Evaluation of various static in vitro-in vivo extrapolation models for risk assessment of the CYP3A inhibition potential of an investigational drug. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014;95:189–98. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2013.187. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grimm SW, Einolf HJ, Hall SD, He K, Lim H-K, Ling K-HJ, Lu C, Nomeir AA, Seibert E, Skordos KW, Tonn GR, Van Horn R, Wang RW, Wong YN, Yang TJ, Obach RS. The Conduct of in Vitro Studies to Address Time-Dependent Inhibition of Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes: A Perspective of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37:1355–1370. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.026716. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

