Insights from imaging the implanting embryo and the uterine environment in three dimensions
- PMID: 27836961
- PMCID: PMC5201036
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.144386
Insights from imaging the implanting embryo and the uterine environment in three dimensions
Abstract
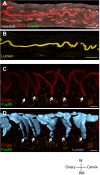
Although much is known about the embryo during implantation, the architecture of the uterine environment in which the early embryo develops is not well understood. We employed confocal imaging in combination with 3D analysis to identify and quantify dynamic changes to the luminal structure of murine uterus in preparation for implantation. When applied to mouse mutants with known implantation defects, this method detected striking peri-implantation abnormalities in uterine morphology that cannot be visualized by histology. We revealed 3D organization of uterine glands and found that they undergo a stereotypical reorientation concurrent with implantation. Furthermore, we extended this technique to generate a 3D rendering of the cycling human endometrium. Analyzing the uterine and embryo structure in 3D for different genetic mutants and pathological conditions will help uncover novel molecular pathways and global structural changes that contribute to successful implantation of an embryo.
Keywords: Blastocyst; Confocal Imaging; Embryo; Implantation; Receptivity; Surface curvature; Uterus; Wnt5a.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Daikoku T., Song H., Guo Y., Riesewijk A., Mosselman S., Das S. K. and Dey S. K. (2004). Uterine Msx-1 and Wnt4 signaling becomes aberrant in mice with the loss of leukemia inhibitory factor or Hoxa-10: evidence for a novel cytokine-homeobox-Wnt signaling in implantation. Mol. Endocrinol. 18, 1238-1250. 10.1210/me.2003-0403 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

