Combined effects of the PNPLA3 rs738409, TM6SF2 rs58542926, and MBOAT7 rs641738 variants on NAFLD severity: a multicenter biopsy-based study
- PMID: 27836992
- PMCID: PMC5234727
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.P067454
Combined effects of the PNPLA3 rs738409, TM6SF2 rs58542926, and MBOAT7 rs641738 variants on NAFLD severity: a multicenter biopsy-based study
Abstract
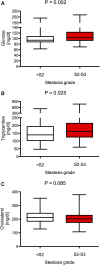
The PNPLA3 p.I148M, TM6SF2 p.E167K, and MBOAT7 rs641738 variants represent genetic risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Here we investigate if these polymorphisms modulate both steatosis and fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. We recruited 515 patients with NAFLD (age 16-88 years, 280 female patients). Liver biopsies were performed in 320 patients. PCR-based assays were used to genotype the PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and MBOAT7 variants. Carriers of the PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 risk alleles showed increased serum aspartate aminotransferase and alanine transaminase activities (P < 0.05). The PNPLA3 genotype was associated with steatosis grades S2-S3 (P < 0.001) and fibrosis stages F2-F4 (P < 0.001). The TM6SF2 genotype was associated with steatosis (P = 0.003) but not with fibrosis (P > 0.05). The MBOAT7 variant was solely associated with increased fibrosis (P = 0.046). In the multivariate model, variants PNPLA3 (P = 0.004) and TM6SF2 (P = 0.038) were associated with steatosis. Fibrosis stages were affected by the PNPLA3 (P = 0.042) and MBOAT7 (P = 0.021) but not by the TM6SF2 polymorphism (P > 0.05). The PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and MBOAT7 variants are associated with increased liver injury. The TM6SF2 variant seems to modulate predominantly hepatic fat accumulation, whereas the MBOAT7 polymorphism is linked to fibrosis. The PNPLA3 polymorphism confers risk of both increased steatosis and fibrosis.
Keywords: adiponutrin; fatty liver; fibrosis; steatosis.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Marchesini G., Petta S., and Dalle Grave R.. 2016. Diet, weight loss, and liver health in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathophysiology, evidence, and practice. Hepatology. 63: 2032–2043. - PubMed
-
- Anstee Q. M., and Day C. P.. 2015. The genetics of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: spotlight on PNPLA3 and TM6SF2. Semin. Liver Dis. 35: 270–290. - PubMed
-
- Krawczyk M., Portincasa P., and Lammert F.. 2013. PNPLA3-associated steatohepatitis: toward a gene-based classification of fatty liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 33: 369–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

