Hippocalcin Is Required for Astrocytic Differentiation through Activation of Stat3 in Hippocampal Neural Precursor Cells
- PMID: 27840601
- PMCID: PMC5083843
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00110
Hippocalcin Is Required for Astrocytic Differentiation through Activation of Stat3 in Hippocampal Neural Precursor Cells
Abstract
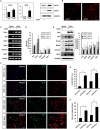
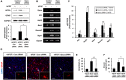
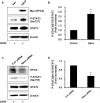
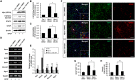
Hippocalcin (Hpca) is a neuronal calcium sensor protein expressed in the mammalian brain. However, its function in neural stem/precursor cells has not yet been studied. Here, we clarify the function of Hpca in astrocytic differentiation in hippocampal neural precursor cells (HNPCs). When we overexpressed Hpca in HNPCs in the presence or absence of bFGF, expression levels of nerve-growth factors such as neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), together with the proneural basic helix loop helix (bHLH) transcription factors NeuroD and neurogenin 1 (Ngn1), increased significantly. In addition, there was an increase in the number of cells expressing glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), an astrocyte marker, and in branch outgrowth, indicating astrocytic differentiation of the HNPCs. Downregulation of Hpca by transfection with Hpca siRNA reduced expression of NT-3, NT-4/5, BDNF, NeuroD, and Ngn1 as well as levels of GFAP protein. Furthermore, overexpression of Hpca increased the phosphorylation of STAT3 (Ser727), and this effect was abolished by treatment with a STAT3 inhibitor (S3I-201), suggesting that STAT3 (Ser727) activation is involved in Hpca-mediated astrocytic differentiation. As expected, treatment with Stat3 siRNA or STAT3 inhibitor caused a complete inhibition of astrogliogenesis induced by Hpca overexpression. Taken together, this is the first report to show that Hpca, acting through Stat3, has an important role in the expression of neurotrophins and proneural bHLH transcription factors, and that it is an essential regulator of astrocytic differentiation and branch outgrowth in HNPCs.
Keywords: astrocyte; differentiation; hippocalcin (Hpca); hippocampal neural precursor cells; signal transducer and activation of transcription 3 (STAT3).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hippocalcin Promotes Neuronal Differentiation and Inhibits Astrocytic Differentiation in Neural Stem Cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2017 Jan 10;8(1):95-111. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.11.009. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Stem Cell Reports. 2017. PMID: 28017654 Free PMC article.
-
NOTCH1-STAT3 signaling axis regulates astrocytic differentiation of hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Jun 8;765:151844. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151844. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40273624
-
MicroRNA-24-3p regulates neuronal differentiation by controlling hippocalcin expression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Nov;76(22):4569-4580. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03290-3. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31486848 Free PMC article.
-
[Priming of neuronal differentiation of cultured neural stem cells by neutrophins].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004 Aug;24(4):181-5. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15484817 Review. Japanese.
-
bHLH transcription factors and mammalian neuronal differentiation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;29(12):1389-99. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(97)89968-2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9570134 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipase D1 Signaling: Essential Roles in Neural Stem Cell Differentiation.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Mar;64(3):333-340. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1042-1. Epub 2018 Feb 24. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29478139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sinomenine attenuates cancer-induced bone pain via suppressing microglial JAK2/STAT3 and neuronal CAMKII/CREB cascades in rat models.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918793232. doi: 10.1177/1744806918793232. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 30027795 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics analysis of periplaque and chronic inactive multiple sclerosis lesions.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Aug 21;17:1448215. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1448215. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39234409 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of human brains with Alzheimer's disease reveals the altered expression of synaptic genes linked to cognitive deficits.Brain Commun. 2021 Jun 3;3(3):fcab123. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcab123. eCollection 2021. Brain Commun. 2021. PMID: 34423299 Free PMC article.
-
MANF Promotes Differentiation and Migration of Neural Progenitor Cells with Potential Neural Regenerative Effects in Stroke.Mol Ther. 2018 Jan 3;26(1):238-255. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29050872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravind P., Chandra K., Reddy P. P., Jeromin A., Chary K. V., Sharma Y. (2008). Regulatory and structural EF-hand motifs of neuronal calcium sensor-1: Mg 2+ modulates Ca 2+ binding, Ca 2+ -induced conformational changes, and equilibrium unfolding transitions. J. Mol. Biol. 376 1100–1115. 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.12.033 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

