Formation and structure of the first metal complexes comprising amidino-guanidinate ligands
- PMID: 27840700
- PMCID: PMC5095825
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016015322
Formation and structure of the first metal complexes comprising amidino-guanidinate ligands
Abstract
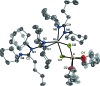
The first metal complexes comprising amidino-guanidinate ligands have been prepared and structurally characterized, namely bis-[μ-N,N',N'',N'''-tetraisopropyl-1-(1-butyl-amidinato)guanidinato-κ3N1,N2:N2]bis-[(tetra-hydro-furan)lithium], [Li2(C18H37N4)2(C4H8O)2], (2), and [bis-(tetra-hydro-furan)-lithium]-di-μ-chlorido-{(N,N'-di-cyclo-hexyl-1-butyl-amidinato-κ2N1,N2)[N,N',N'',N'''-tetra-cyclo-hexyl-1-(1-butyl-amidinato)guanidinato-κ2N1,N2]holmate(III)}, [HoLiCl2(C4H8O)2(C17H31N2)(C30H53N4)], (3). The novel lithium amidino-guanidinate precursors Li[ n BuC(=NR)(NR)C(NR)2] [1: R = Cy (cyclo-hex-yl), 2: R = i Pr) were obtained by treatment of N,N'-diorganocarbodi-imides, R-N=C=N-R (R = i Pr, Cy), with 0.5 equivalents of n-butyl-lithium under well-defined reaction conditions. An X-ray diffraction study of 2 revealed a ladder-type dimeric structure in the solid state. Reaction of anhydrous holmium(III) chloride with in situ-prepared 2 afforded the unexpected holmium 'ate' complex [ n BuC(=NCy)(NCy)C(NCy)2]Ho[ n BuC(NCy)2](μ-Cl)2Li(THF)2 (3) in 71% yield. An X-ray crystal structure determination of 3 showed that this complex contains both an amidinate ligand and the new amidino-guanidinate ligand.
Keywords: amidinate ligands; amidinoguanidinate; crystal structure; guanidinate ligands; holmium; lithium.
Figures
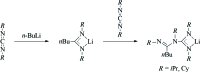

References
-
- Agilent (2011). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
-
- Aharonovich, S., Kapon, M., Botoshanski, M. & Eisen, M. S. (2008). Organometallics, 27, 1869–1877.
-
- Bailey, P. J. & Pace, S. (2001). Coord. Chem. Rev. 214, 91–141.
-
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Chlupatý, T., Padělková, A., Lyčka, A. & Růžička, A. (2011). J. Organomet. Chem. 696, 2346–2354.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
