STAT3 inhibitor, cucurbitacin I, is a novel therapeutic agent for osteosarcoma
- PMID: 27840900
- PMCID: PMC5117998
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3757
STAT3 inhibitor, cucurbitacin I, is a novel therapeutic agent for osteosarcoma
Abstract
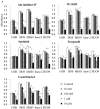
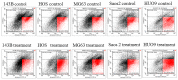
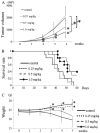
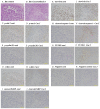
The development of clinical agents remains a costly and time-consuming process. Although identification of new uses of existing drugs has been recognized as a more efficient approach for drug discovery than development of novel drugs, little screening of drugs that might be used for a rare malignant tumor such as osteosarcoma (OS) has been performed. In this study, we attempted to identify new molecular targeted agents for OS by employing Screening Committee of Anticancer Drugs (SCADS) kits. To screen compounds for OS treatment, their effect on cell viability of the OS cell lines 143B, MG63, HOS, SAOS-2, and HUO9 were evaluated. Candidate drugs were narrowed down based on a global anti-proliferative effect against these five OS cell lines. After excluding cytotoxic compounds and compounds unsuitable for in vivo administration, cucurbitacin I was extracted. Cucurbitacin I has been found to have cytotoxic and anti-proliferative properties against several tumors through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation. Cucurbitacin I dose- and time-dependently inhibited the proliferation of all five OS cell lines. Following cucurbitacin I treatment, STAT3 was inactivated and analysis of Mcl-1, cleaved PARP and caspase-3 indicated apoptosis induction. Expression of cell cycle regulator proteins, such as phospho-cyclin D1, c-Myc and survivin, were suppressed. Finally, cucurbitacin I potently inhibited the tumor growth of human OS 143B cells in nude mice. Our in vitro and in vivo results suggest that STAT3 inhibition by cucurbitacin I will be an effective and new approach for the treatment of OS.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Alternol, a natural compound, exerts an anti-tumour effect on osteosarcoma by modulating of STAT3 and ROS/MAPK signalling pathways.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Feb;21(2):208-221. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12957. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27624867 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me induces apoptosis in multidrug resistant osteosarcoma cells through inhibition of Stat3 pathway.BMC Cancer. 2010 May 10;10:187. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-187. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20459702 Free PMC article.
-
Cucurbitacin B, a small molecule inhibitor of the Stat3 signaling pathway, enhances the chemosensitivity of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Sep 1;641(1):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.04.062. Epub 2010 May 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20483353
-
STAT3 and its targeting inhibitors in osteosarcoma.Cell Prolif. 2021 Feb;54(2):e12974. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12974. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Cell Prolif. 2021. PMID: 33382511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids Active Against Osteosarcoma: A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms Involved.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(13):1993-2001. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170214115718. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28201973 Review.
Cited by
-
JSI-124 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Regulates the Apoptosis in Glioblastoma Cells.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 8;11(11):2999. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11112999. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38001999 Free PMC article.
-
TTC36 inactivation induce malignant properties via Wnt-β-catenin pathway in gastric carcinoma.J Cancer. 2021 Mar 5;12(9):2598-2609. doi: 10.7150/jca.47292. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33854620 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and phenotypic determinants of morphologies in 3D cultures and xenografts of lung tumor cell lines.Cancer Sci. 2023 Apr;114(4):1757-1770. doi: 10.1111/cas.15702. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36533957 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of STAT3 blocks protein synthesis and tumor metastasis in osteosarcoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 4;37(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0914-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30286779 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Targeting of STAT3 Orchestrated Lipid Metabolism in Therapy-Resistant Cancers.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 28;10(8):1118. doi: 10.3390/biom10081118. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32731620 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meyers PA, Heller G, Healey J, Huvos A, Lane J, Marcove R, Applewhite A, Vlamis V, Rosen G. Chemotherapy for nonmetastatic osteogenic sarcoma: The Memorial Sloan-Kettering experience. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Harris MB, Gieser P, Goorin AM, Ayala A, Shochat SJ, Ferguson WS, Holbrook T, Link MP. Treatment of metastatic osteosarcoma at diagnosis: A Pediatric Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:3641–3648. - PubMed
-
- Meyers PA, Heller G, Healey JH, Huvos A, Applewhite A, Sun M, LaQuaglia M. Osteogenic sarcoma with clinically detectable metastasis at initial presentation. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11:449–453. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

